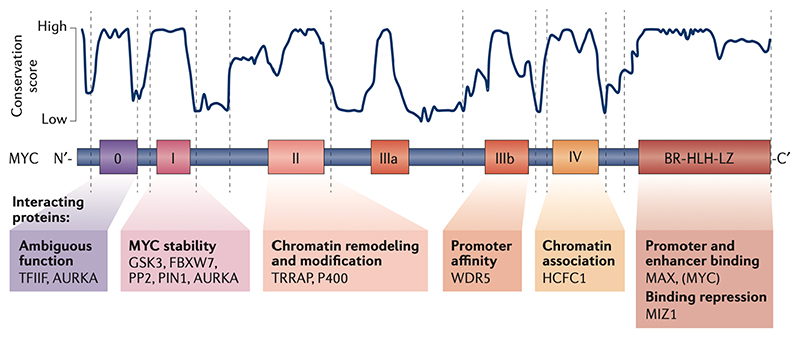
Figure 1. Protein domains of MYC and their canonical function.
Amino acid sequence analysis identified different degrees of conservation within MYC proteins. While the C-terminal domain responsible for DNA binding is entirely conserved only small stretches – the MYC boxes – show a high degree of conservation in the remaining part of the protein. The conservation score shown in the figure was calculated as described in REF 126. Function definitions of MYC boxes 0–IV are based on deletion and/or point mutations. Examples of proteins that interact with the relevant MYC boxes are indicated. AURKA, Aurora kinase A; BR, basic region; FBXL3, F-box and leucine rich repeat protein 3; FBXW7, F-box and WD repeat domain containing 7; GSK3,glycogen synthase kinase 3; HCFC1, host cell factor C1; MAX MYC associated factor X; MIZ1,MYC interacting zing finger protein 1; P400, E1A binding protein p400 ; PIN1, peptidylprolyl cis/trans isomerase NIMA-interaction 1; PP2A, serine/threonine protein phosphatase 2A; TFIIF, general transcription factor IIF subunit 1; TRRAP, transformation/transcription domain associated protein; WDR5, WD repeat domain 5.