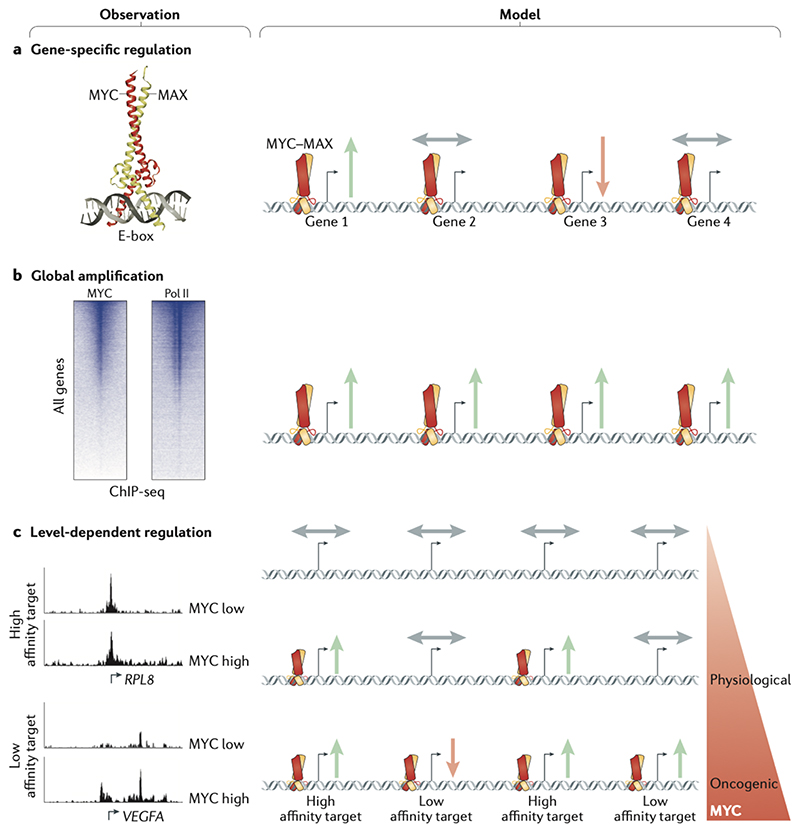
Figure 2. Models of gene regulation by MYC.
(a) Specific-gene regulation: Based on the study and structural elucidation of the Enhancerbox (E-box) binding by MYC, specific MYC-induced target genes were discovered and characterized. (b) Global gene activation: Genome-wide chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-seq) studies of MYC identified that MYC binds at the promoters of most RNA polymerase II (Pol II)-bound and expressed genes. Accordingly, Myc induces a global increase in cellular mRNA levels in some biological systems. (c) Gene-specific affinity: Although MYC binding is detectable at most promoters, promoter affinities for MYC differ widely. Genes with high promoter–MYC affinity are bound and upregulated by MYC at physiological levels, but are not further induced at oncogenic levels, as binding is already saturated. Instead, oncogenic MYC upregulates low affinity target genes. The affinity model can reconcile the seemingly opposing specific gene and global gene models. Green arrows indicate activation, red arrow indicates repression and grey arrows indicate no regulation of genes. RPL8, 60S ribosomal protein L8; VEGFA, vascular endothelial growth factor A.