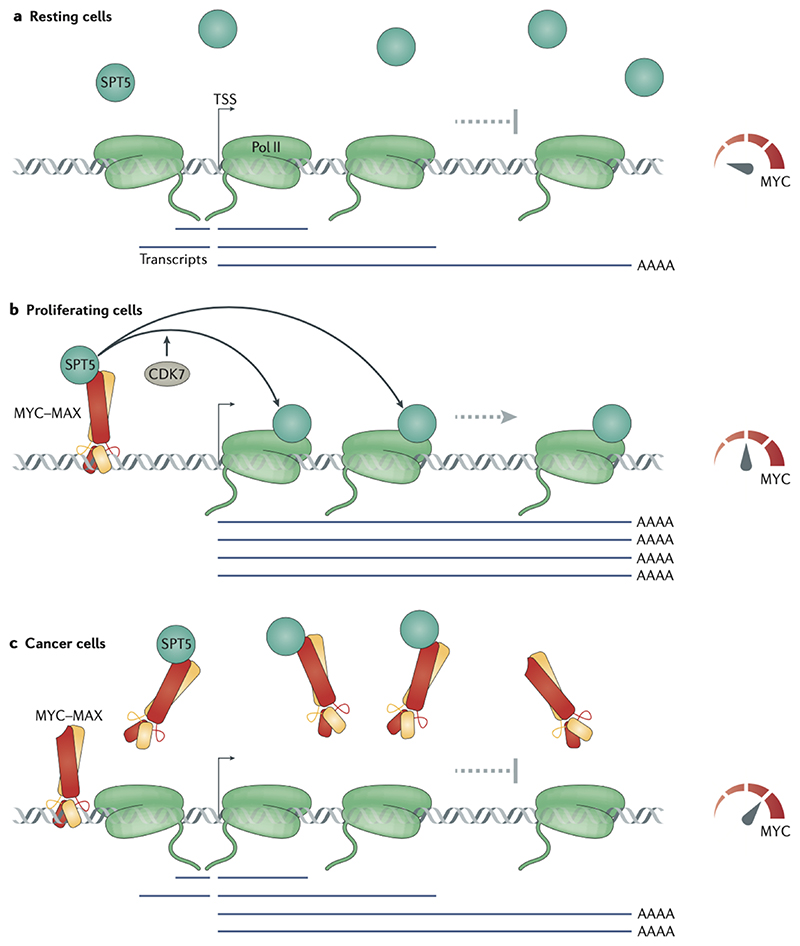
Figure 4. A handover-model of promoter-proximal function of MYC proteins.
(a) In resting cells, which do not express MYC, the transcription elongation factor SPT5 is insufficiently recruited to RNA polymerase II (Pol II), which loses directionality and processivity, resulting in increase in the levels of antisense and abortive transcripts. (b) In growing cells, MYC is expressed, binds SPT5 and recruits it to promoters. The transfer of SPT5 from MYC to Pol II depends on cyclin-dependent kinase 7 (CDK7).Pol II associated with transcription elongation factors engages in productive (fast, processive and directional) transcription elongation and produces full-length mRNAs. (c) In cancer cells expressing high levels of MYC, a considerable fraction of SPT5 is sequestered by soluble MYC, and transcription is decreased at known MYC-repressed genes. TSS, transcription start site.