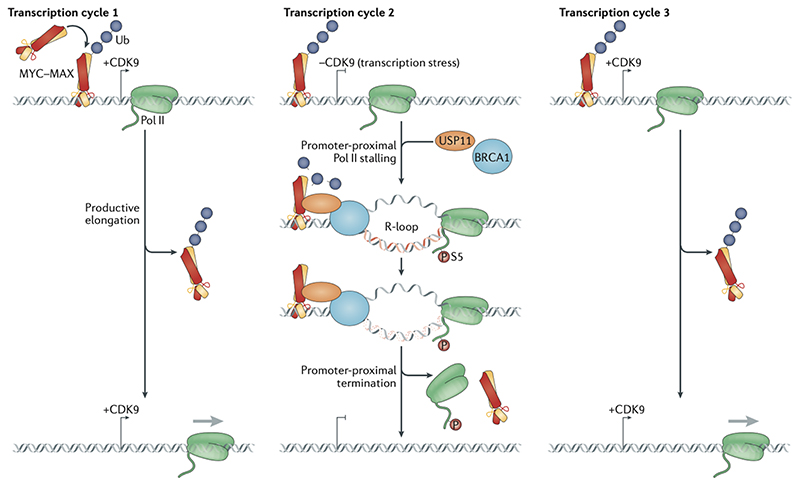
Figure 5. MYC binding at core promoters.
Model of global and possibly crucial functions of MYC proteins at all active promoters with very small effects on steady-state mRNA levels. MYC ubiquitylation allows cyclin-dependent kinase 9 (CDK9)-driven RNA polymerase II (Pol) II to generate the mRNA (Transcription Cycle # 1). However, in response to transcription stress, which induces or augments promoter-proximal Pol II stalling and R-loop formation, BRCA1 is recruited to the R-loop with the help of USP11, which de-ubiquitylates MYC, thereby allowing it to interact with BRCA1 (Transcription cycle # 2). This promotes the resolution of the R-loop and dissociation of the Pol II machinery, which makes the promoter ready for a new cycle where Pol II can again transcribe in a CDK9 driven manner (Transcription cycle # 3).