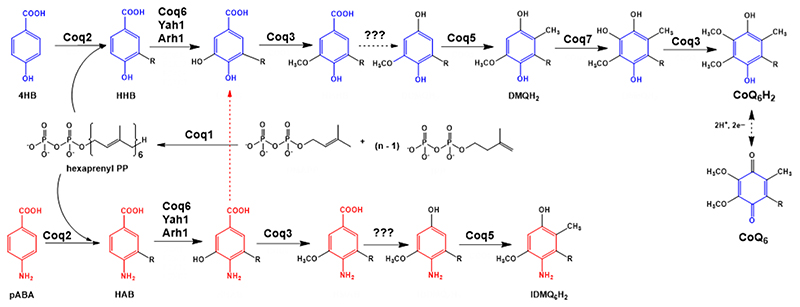
Figure 1. Coenzyme Q biosynthetic pathway in S. cerevisiae.
Adapted from [1]. At least 13 proteins are necessary for efficient CoQ biosynthesis in S. cerevisiae (Coq1-11, Yah1 and Arh1) [1]. The polyprenyl diphosphate is produced by a hexaprenyl diphosphate synthase (Coq1) [6]. Coq2 mediates the condensation of the isoprenoid tail with the aromatic ring precursor, generating a membrane-bound CoQ intermediate. In yeast, both 4HB and pABA can be used as ring precursors for CoQ6 biosynthesis [7, 8]. Intermediates originating from 4HB are depicted in blue, while intermediates originating from pABA are depicted in red. Several Coq proteins (Coq6, Coq3, Coq5 and Coq7) modify the hexaprenylated CoQ precursor to form the final product. Other Coq proteins (Coq4, Coq8, Coq9, CoQ10 and Coq11) are essential for efficient CoQ production. For simplicity, only the relevant intermediates to understand further analysis have been named. 4HB = 4-hydroxybenzoic acid; pABA = para-aminobenzoic acid; HHB = 3-hexaprenyl-4-hydroxybenzoic acid; HAB = 3-hexaprenyl-4-aminobenzoic acid; DMQH2 = demethoxy-QH2; IDMQH2 = 4-imino-demethoxy-QH2; CoQ6H2 = reduced coenzyme Q6H2; CoQ6 = oxidized coenzyme Q6.