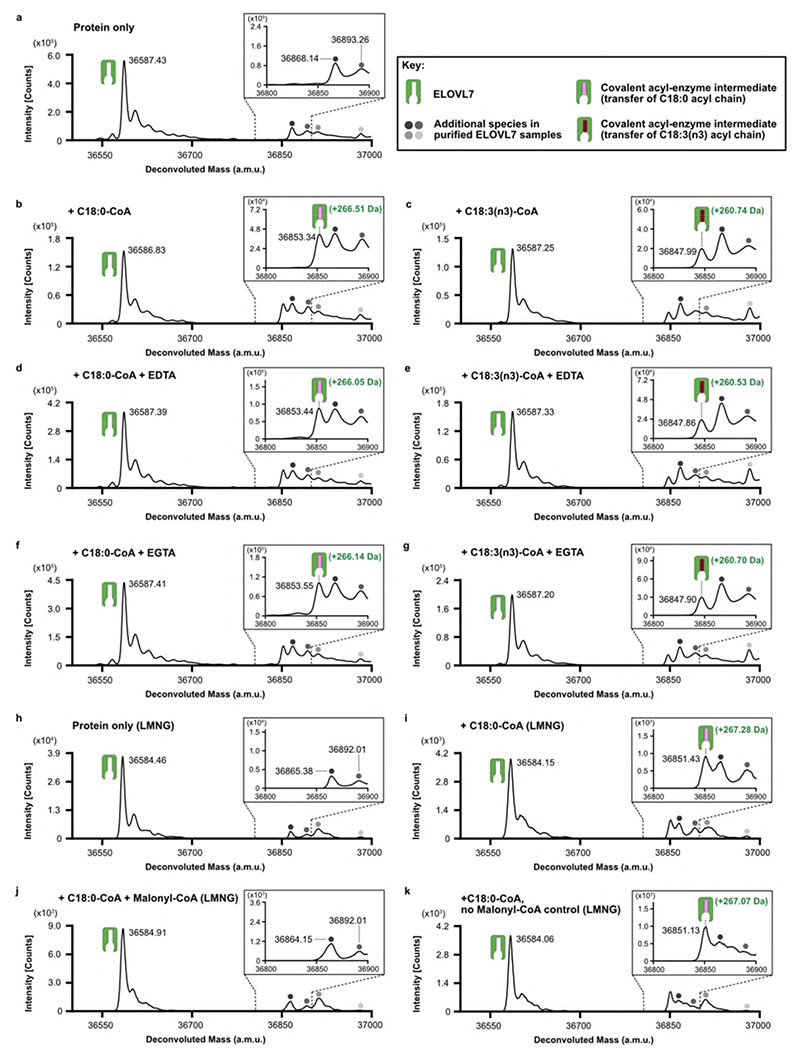
Extended Data Fig. 6. Identification of a covalent acyl-enzyme intermediate of ELOVL7.
Purified, tagged, wildtype ELOVL7 was incubated in the presence and absence of known substrates and metalchelating agents prior to LC-ESI-MS intact mass analysis. a-g, Deconvoluted intact mass spectra for ELOVL7 incubated for 2h at 37°C. a, in the absence of substrates. b, ELOVL7 incubated with 100μM C18:0-CoA. Expected mass addition for acyl intermediate upon reaction with C18:0-CoA: +266.47 Da. c, ELOVL7 incubated with 100μM C18:3(n3)-CoA. Expected mass addition for acyl intermediate upon reaction with C18:3(n3)-CoA: +260.42 Da. d-e, ELOVL7 incubated with d, 100μM C18:0-CoA or e, 100μM C18:3(n3)-CoA in the presence of 1mM EDTA. f-g ELOVL7 incubated with f, 100μM C18:0-CoA or g, 100μM C18:3(n3)-CoA in the presence of 1mM EGTA. h-k, Sequential reaction of LMNG-purified ELOVL7 with C18:0-CoA and malonyl-CoA. h, LMNG-purified ELOVL in the absence of substrates. i, ELOVL7 incubated with 100μM C18:0-CoA. j, Purified ELOVL7 initially incubated with 100μM C18:0-CoA, followed by incubation with 200 μM malonyl-CoA. Addition of the second substrate leads to loss of the acyl-enzyme intermediate peak, consistent with the reaction having gone to completion. k, control ELOVL7 sample taken after incubation with C18:0-CoA was further incubated in the absence of malonyl-CoA, showing that covalent intermediate loss only occurs in the presence of malonyl-CoA. All experiments were repeated independently twice with similar results (n=2 biological repeats, see Supplementary Figure 1 and Figure 2 for replicate traces. See Supplementary Table 2 for theoretical and experimental masses and mass errors).