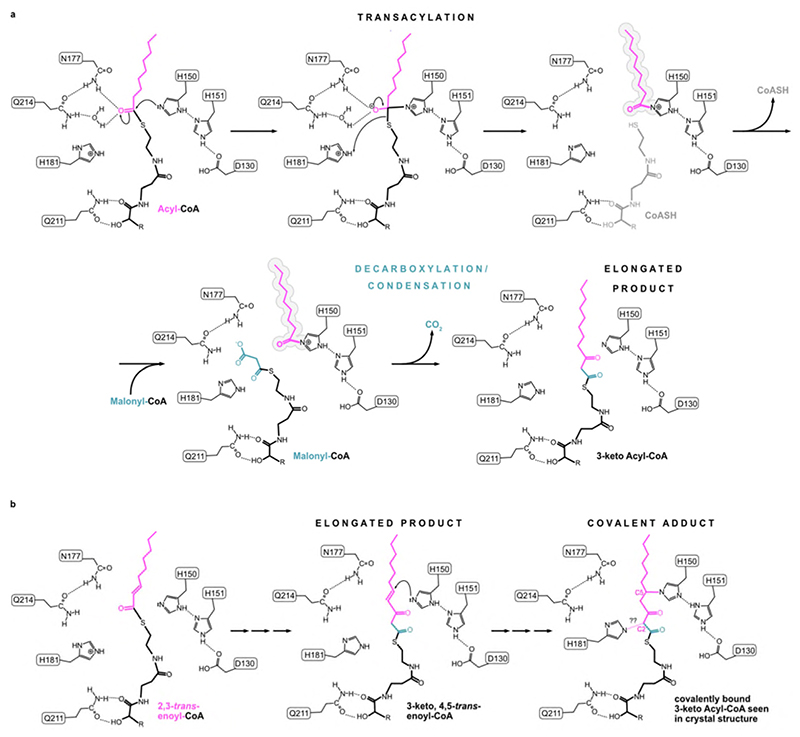
Extended Data Fig. 7. Proposed ping-pong reaction mechanism for ELOVL7.
a, Transacylation step with acyl chain of first substrate being transferred to H150. In the second step, malonyl-CoA binds and undergoes decarboxylation and a condensation reaction to form the elongated 3-keto product. b, Proposed reaction steps leading to C-N covalent adduct with H150 seen in crystal structure. In this scenario a 2,3-trans-enoyl-CoA serves as the first substrate (left) leading to the 3-keto,4,5-trans-enoyl-CoA ‘product’ (middle) which subsequently crosslinks to H150 via a conjugate addition reaction of H150 (right). The nature of the reaction that leads to H181 crosslinking to the C2 atom of the 3-keto-acyl-CoA is not clear.