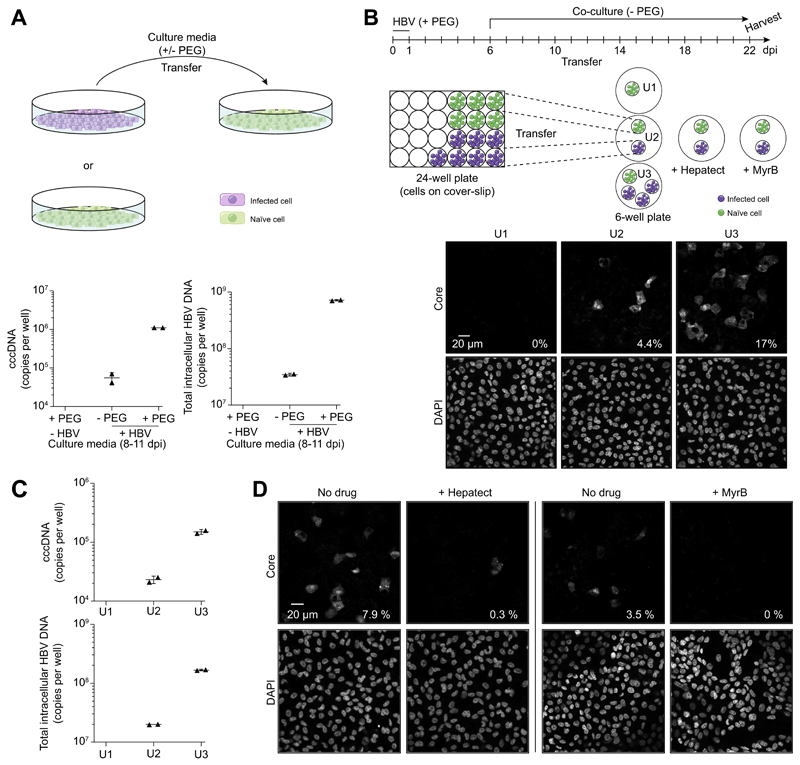
Fig. 4. Analysis of de novo infection mediated by extracellular virions.
(A) Cell culture media from HBV-infected HepG2-NTCP-K7 cells were transferred onto naïve cells with or without PEG. At 11 days post-transfer, cccDNA and total intracellular HBV-DNA were analyzed by qPCR. (B) For co-culture experiments in a physically separated setting, HepG2-NTCP-K7 cells were seeded on coverslips and either treated with PEG only or infected with HBV at an moi of 1,000 vp/cell with PEG. At 6 dpi, coverslips with infected cells were transferred into new wells together with coverslips with non-infected cells as depicted and subsequently co-cultured for 16 days in the absence of PEG. Naïve target cells from each condition (denoted U1, U2 and U3) were subjected to immunofluorescence staining with an anti-core antibody. (C) cccDNA and total intracellular HBV-DNA contents were analyzed by qPCR. Target cells were treated with trypsin for 5 min to remove cell surface bound HBV prior to DNA isolation. (D) The same experiment performed (condition U2) in the presence or absence of entry inhibitors (0.5 IU/ml Hepatect CP or 200 nM MyrB). The percentage of infected cells is denoted at the bottom-right corner of each image. cccDNA, covalently closed circular DNA; dpi, day post-infection; HBV, hepatitis B virus; moi, multiplicity of infection; MyrB, Myrcludex-B; PEG, polyethylene glycol; qPCR, real-time PCR; vp, virus particle. (This figure appears in colour on the web.)