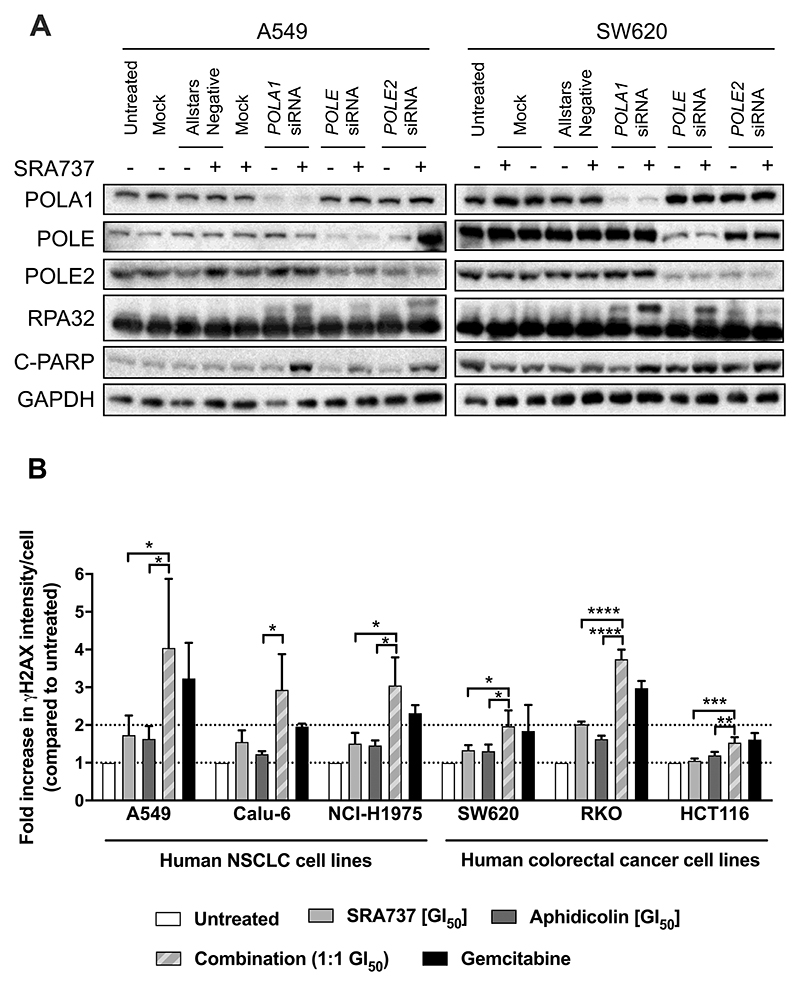
Figure 5. Combined CHK1 and DNA polymerase inhibition increases replication stress and DNA damage in cancer cells.
A Levels of RPA32 and C-PARP in the lysate of NSCLC A549 and colorectal cancer SW620 cells transfected with 0.1 nM (A549) or 1 nM (SW620) POLA1 #3, POLE #2 or POLE2 #4 siRNA for 48 h prior to 24 h treatment with SRA737. A549 cells were treated with 0.4 μM SRA737 and SW620 cells with 0.8 μM. RPA32 band shift is indicative of replication stress and C-PARP is a marker of apoptosis. GAPDH was used as loading control. Data are representative of two independent experiments. The blot has been cropped for clarity. B Mean (± SD) γH2AX level, relative to that in untreated cells, in cancer cells treated with aphidicolin, SRA737 alone or a 1:1 combination of both agents for 24 h. γH2AX levels were determined by immunofluorescence using an IN Cell Analyser (n = ≥3). Pair-wise comparisons of levels in different treatment groups were carried out using an unpaired students t-test, *p = <0.05, **p = <0.01, ***p = <0.001, ****p = <0.0001.