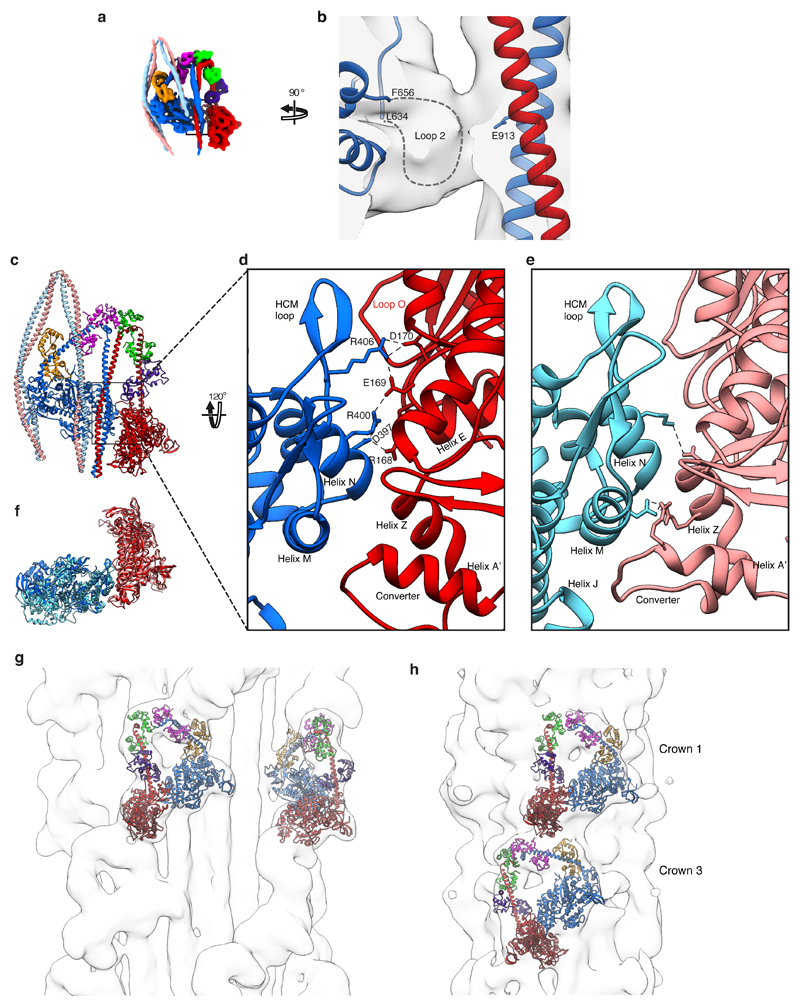
Extended Data Figure 5. Interaction between loop 2 (blocked-head motor) and segment-1, the motor-motor interface of the IHM and fit of the SmM IHM structure into filament cryoEM density maps for tarantula and cardiac myosin filaments.
a-b, EM density map reveals an interaction interface between segment-1 and density attributable to the blocked-head motor loop 2 (dashed line). E913 in segment-1 is highlighted for reference. Map contour level 0.17. c. Overall model to show region of interest, the motor-motor interface (boxed). d, Ionic interactions across this interface, involving Helix N and HCM loop of the blocked-head motor with 3 successive residues (168-170) close to Helix E in the free-head motor (Supplementary Video 5). e, The same region of interest from a recent cardiac IHM pseudo-atomic model15. f, Superimposition of the motor domains for our structure, and for the cardiac IHM pseudo-atomic model15 aligned on the free-head (red/pink) with view as in d. The blocked head of the cardiac IHM (cyan) is rotated counter-clockwise compared to that for SmM (blue) g, h, Fit of the paired heads of the pseudo-atomic model of shutdown SmM into the IHM motifs of reconstructions of thick filaments, using Chimera. The filament axis is vertical and the filament tip is at the top of the page. g, The fit to 20 Å map of tarantula thick filaments, EMD-195043, contour level 28.6). h. The fit to 28 Å map of cardiac thick filaments (EMD-2240 14, contour level 0.14).