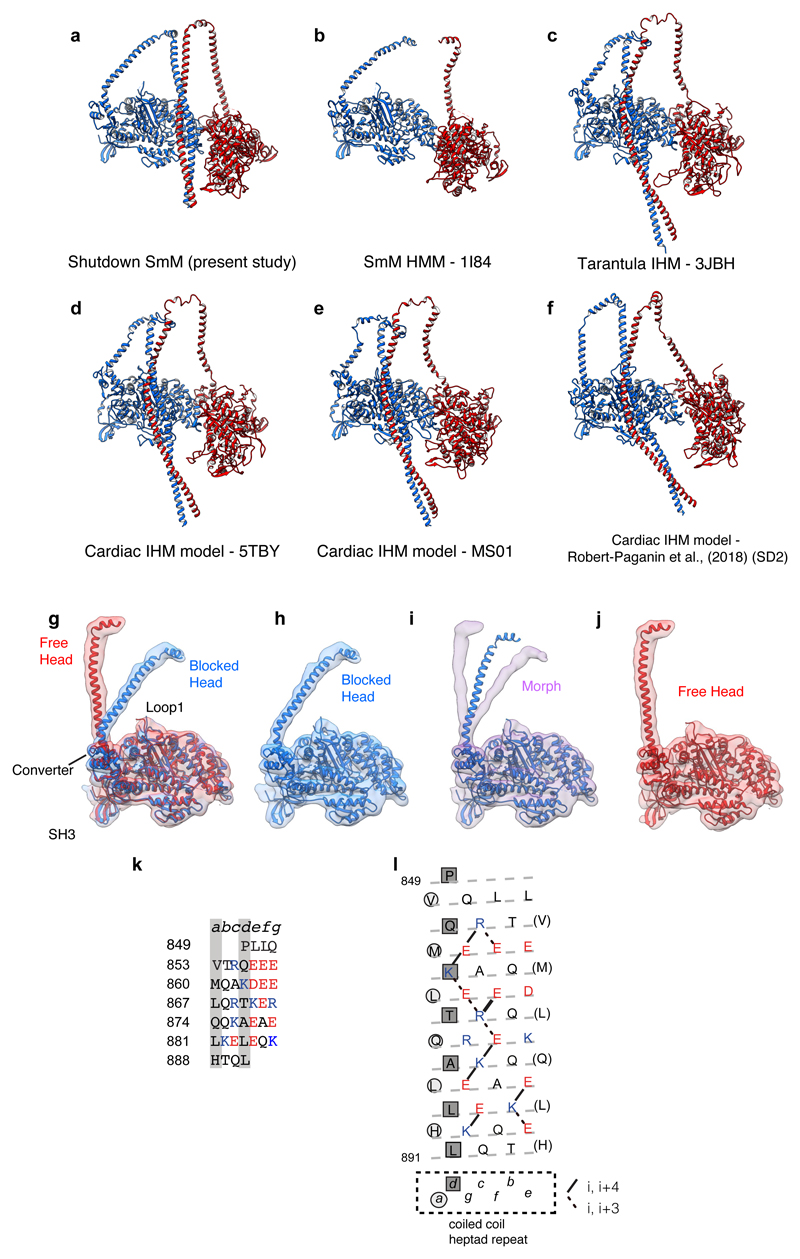
Extended Data Figure 4. Comparisons of IHM pseudo-atomic models, free- and blocked-heads and the SAH-domain character of start of segment-1.
a-f, Comparison of pseudo-atomic models of the IHM with LCs omitted to allow comparison of LCD heavy-chain structure. a, Pseudo-atomic model of SmM from the present study. b, Model (PDB id 1I84) produced from SmM heavy meromyosin IHM 2D crystal 20Å map7; tentative assignment of tail omitted. c, Model (PDB id 3JBH) produced from IHM of tarantula thick filament 20Å map40, fitted with tarantula sequence. d, Model (PDB id 5TBY) proposed for human cardiac IHM by homology modelling the cardiac amino acid sequences on the tarantula model14. e, Model (downloaded from Spudich lab website as MS01.pdb) of human cardiac myosin IHM (produced by use of homology models fitted to tarantula IHM model 3DTP15). f, Model (downloaded as Supplementary Data 2) for cardiac IHM produced by use of a cardiac motor domain-ELC crystal structure (5N69) and homology model of RLC fitted into the tarantula thick filament IHM 20Å map31. g, Superposition of free- and blocked-head motors (up until pliant region) showing how the LCD regions differ between the heads (without light chains shown), segmented maps and model for motor domains shown. h, Blocked-head motor, model in map, i morph between blocked-head and free-head model and maps (shown without light chains), j Free-head model in map. Map contour level 0.28 (Supplementary Video 3). k, SmM heavy-chain sequence at the start of the predicted coiled coil. Coiled-coil seam a and d residues marked by grey stripes; acidic residues red, basic residues blue. i, Heptad net projection of sequence 35 in which the dashed line shows the path of the polypeptide backbone as α-helix, circles and squares indicate the a and d positions of the heptad repeat and every seventh residue is repeated (in brackets) to allow all ionic interactions to be mapped.