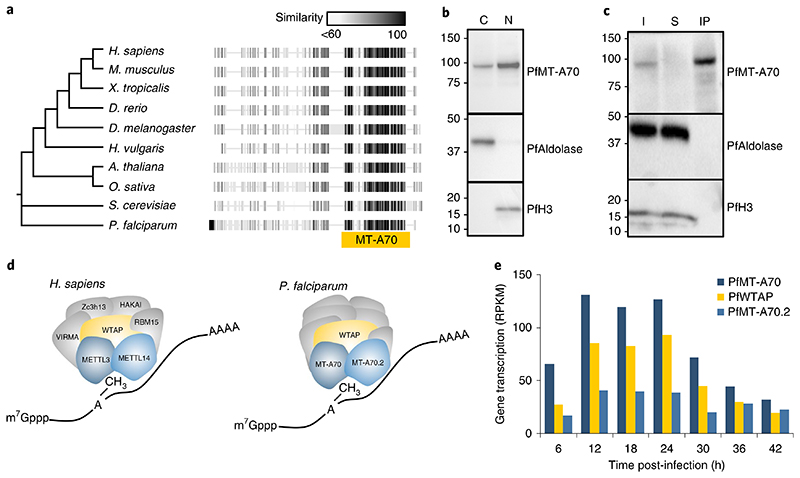
Fig. 2. Characterization of the P. falciparum m6A writer complex.
a, Phylogenetic tree and protein alignments of PfMT-A70 with orthologues in other eukaryotes. The location of the MT-A70 domain is shown below the alignment (yellow bar). The grey-scale gradient indicates the percentage similarity across all proteins at an aligned position. b, Western blot analysis showing the enrichment of HA-tagged PfMT-A70 in the cytoplasmic (C) and nuclear (N) cell fractions at 12 h.p.i. PfAldolase and histone H3 serve as controls for the cytoplasmic and nuclear fraction, respectively. Numbers on the left indicate molecular weight in kilodaltons. Data are representative of three independent biological experiments. c, Western blot analysis of PfMT-A70-HA co-IP with anti-HA antibodies. PfAldolase and histone H3 demonstrate efficacy of the anti-HA co-IP. Numbers on the left indicate molecular weight in kilodaltons. I, input; S, supernatant; IP, co-IP fraction. Data are representative of three independent biological experiments. d, Schematic of the human m6A writer complex (left) and the P. falciparum proteins that were co-immunoprecipitated with PfMT-A70. Orthologous proteins are highlighted in the same colour; that is, METTL3/PfMT-A70, METTL14/PfMT-A70.2 and WTAP/PfWTAP. Co-factors of the human core m6A writer complex (left) and putative, non-conserved co-factors of P. falciparum (right) are shown in grey. e, Gene transcription (in reads per kilobase of exon per one million mapped reads (RPKM))82 of putative orthologues of the P. falciparum m6A writer complex at 6-h intervals over the course of the IDC.