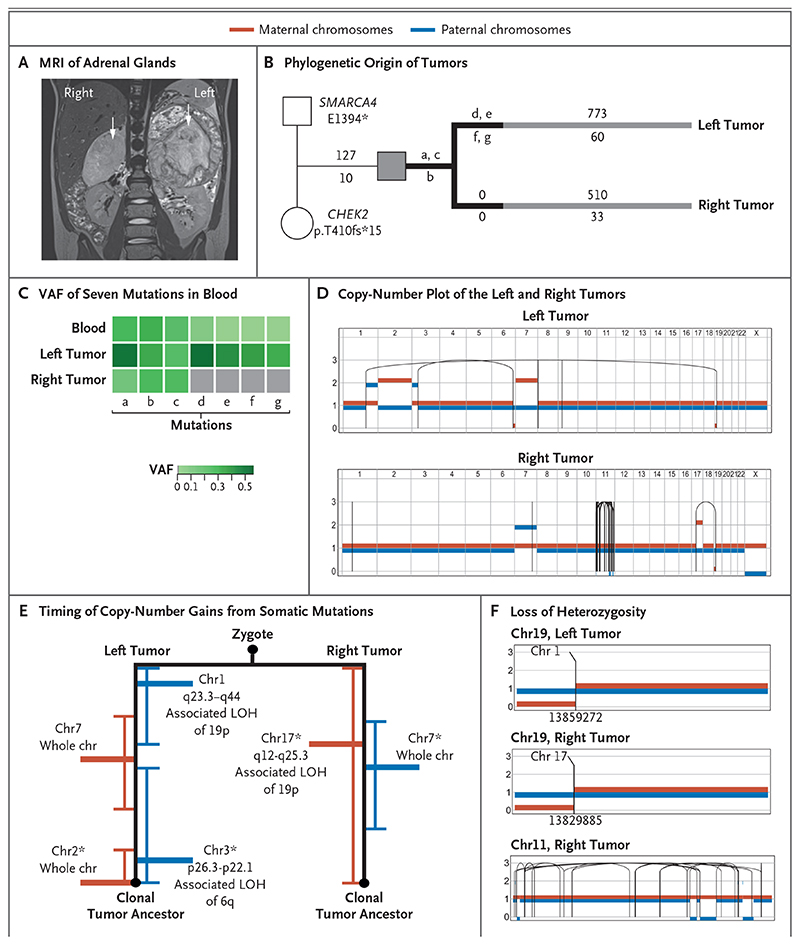
Figure 2. Independent Origin and Convergent Parallel Evolution of Tumors in Patient 1.
Panel A shows coronal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the right and left adrenal glands in Patient 1 (case number, PD36812), with large tumors indicated by white arrows. Panel B shows the phylogenetic origins of the right and left tumors in Patient 1. The patient inherited two pathogenic variants: a truncating missense variant in SMARCA4 from the father and a truncating frameshift CHEK2 variant from the mother. Branches in black depict variants (labeled a through g) in the tumors that were shared with blood. The numbers of substitutions are annotated above the branch, and insertions or deletions (indels) are annotated below the branch. Panel C shows the variant allele frequency (VAF) of the seven mutations present in blood (labeled a through g, as in the phylogenetic tree). Panel D shows a phased copy-number plot of the left and right adrenal tumors. Breakpoints of structural variants are connected by solid lines. In the right tumor, the dense grouping of solid lines on chromosome 11 is the result of chromothripsis. Panel E shows the timing of the acquisition of copy-number gains from somatic mutations before and after duplication. Gains of maternal chromosomes (chr) are indicated in red and gains of paternal chromosomes in blue. Within each branch, asterisks highlight pairs of rearrangements that are unlikely to have occurred at different time points (P>0.05 by the Poisson test). LOH denotes loss of heterozygosity. Panel F shows the different breakpoints that underlie the loss of heterozygosity of chromosome 19 in the left and right tumors. Only the right tumor shows signs of chromothripsis. Translocations that mediate a loss of heterozygosity on chromosome 19p in the left and right tumors have different chromosomal partners and are located in different genomic positions, as indicated by the numbers below the breakpoints.