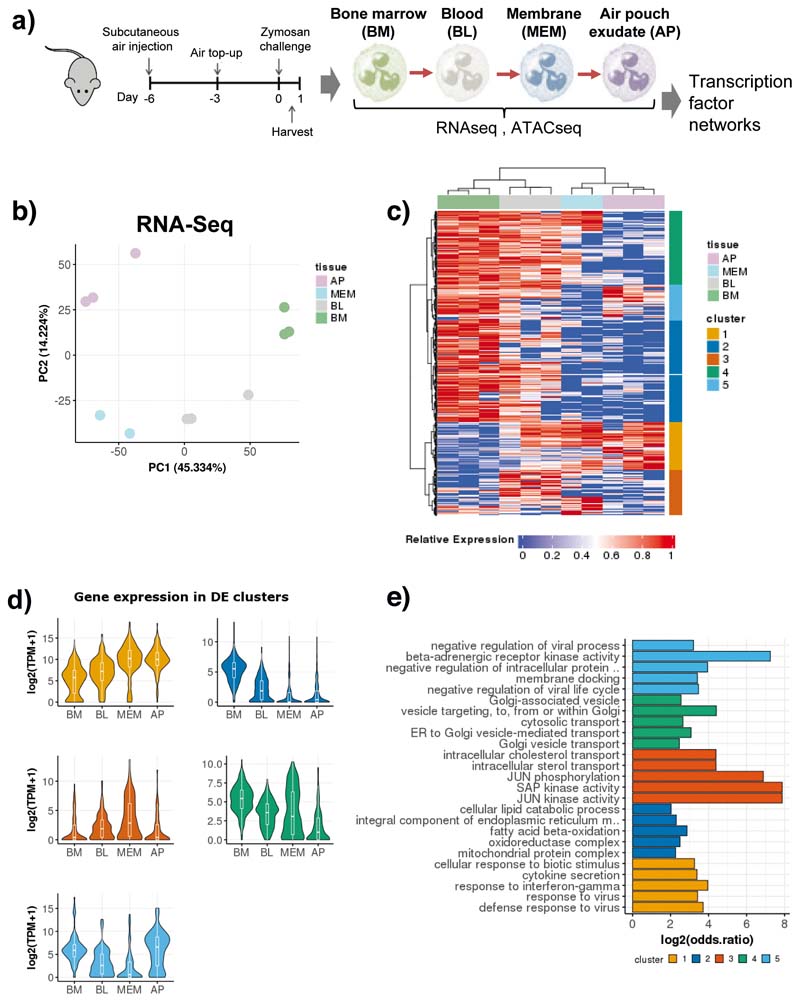
Fig. 1. Neutrophil transcriptional re-wiring en route to the site of inflammation is parsimonious.
a) Ly6Ghi CD11b+ cells were sorted from the bone marrow, blood, air pouch membrane, and air pouch exudate in mice subjected to air pouch model and zymosan challenge for 4 hours. Small bulk RNA-seq analysis powered by Smart-seq2 library preparations52 for transcriptional changes and ATAC-seq analysis for chromatin changes were conducted.
b) Principal component analysis (PCA) of 1,865 differentially expressed genes derived from small bulk RNA-seq analysis (n=300 cells / sample) of neutrophils isolated from the bone marrow, blood, membrane and exudate of two mice subjected to the air pouch model and zymosan challenge.
c) Hierarchical clustering of all differentially expressed genes (LRT test, padj < 0.01), based on Manhattan distances using the Ward method. Data are presented as heatmap normalised to the minimum and maximum of each row.
d) Violin plots showing the expression of all genes within each cluster identified in B) across different compartments from two mice. For the box plot within each violin plot, middle lines indicate median values, boxes range from the 25th to 75th percentiles, and upper/lower whiskers extend from the hinge to the largest/smallest value no further than 1.5 times the interquartile range (IQR) from the hinge.
e) Gene ontology (GO) analysis, showing the top 5 enriched GO categories for each cluster from Fig. 1c).