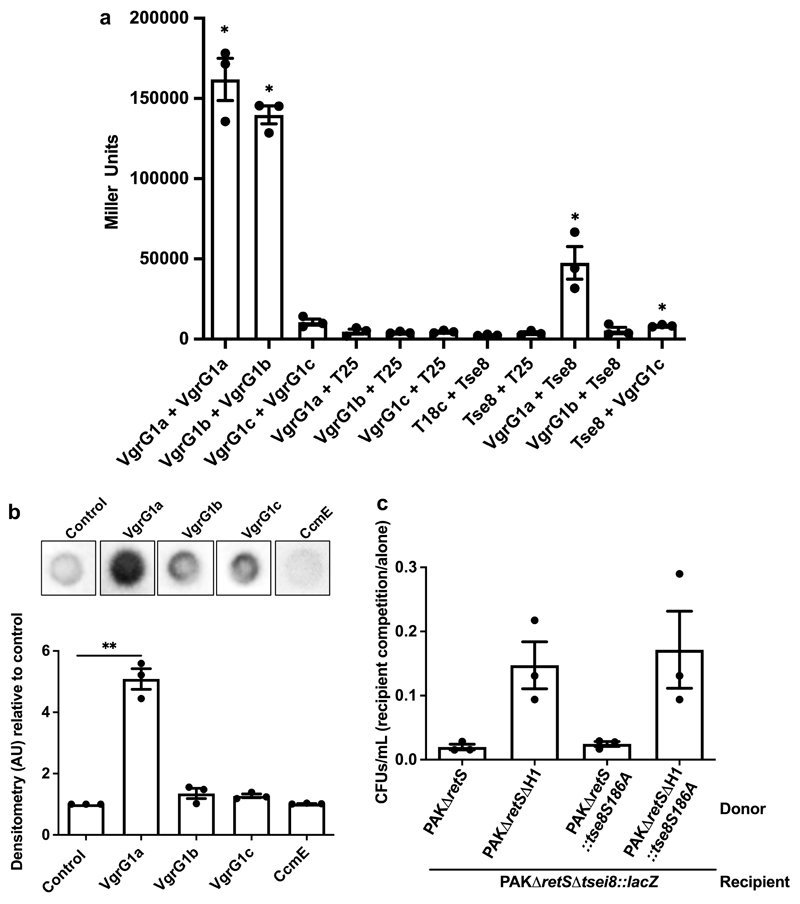
Figure 2. Tse8 interacts with VgrG1a and does not require putative catalytic residue for toxicity.
a, BTH assays were used to quantify the level of interaction between Tse8 and VgrGs with β-galactosidase activity assays performed on the cell lysates of each interaction pair. b, Tse8 interacts with VgrG1a in dot blot assays (top panel). Densitometry quantifications of Tse8 interactions with respective partners (bottom panel). CcmE-His is used as a non-specific binding control. c, Tse8 toxicity is not dependent on the conserved putative catalytic residue S186. Competition assays were performed with donors PAKΔretS, PAKΔretSΔH1, PAKΔretS::tse8S186A or PAKΔretSΔH1::tse8S186A and recipient PAKΔretSΔtsei8::lacZ. Statistical analyses: (a) Mean ± SEM of three biological replicates performed in triplicate (n=3). One-way Anova with Tukey’s multiple comparison post-test, * P<0.05 compared to the Miller units for each of VgrG1a, VgrG1b, VgrG1c and Tse8 with the respective T18c or T25 partner. (b) Densitometry measurements normalized to the control and represented as the Mean ± SEM from three independent replicates (n=3). Two-tailed student’s t-test, ** P<0.005 compared to control; ns between control and VgrG1b (P=0.169), VgrG1c (P=0.067) and CcmE (P=0.159). (c) Mean CFUs/mL ± SEM of recovered recipient are represented from three independent replicates performed in triplicate (n=3). Two-tailed student’s t-test, * P<0.05 for PAKΔretS compared to PAKΔretSΔH1 and PAKΔretSΔH1::tse8S186A; ns between PAKΔretS and PAKΔretS::tse8S186A (P=0.226).