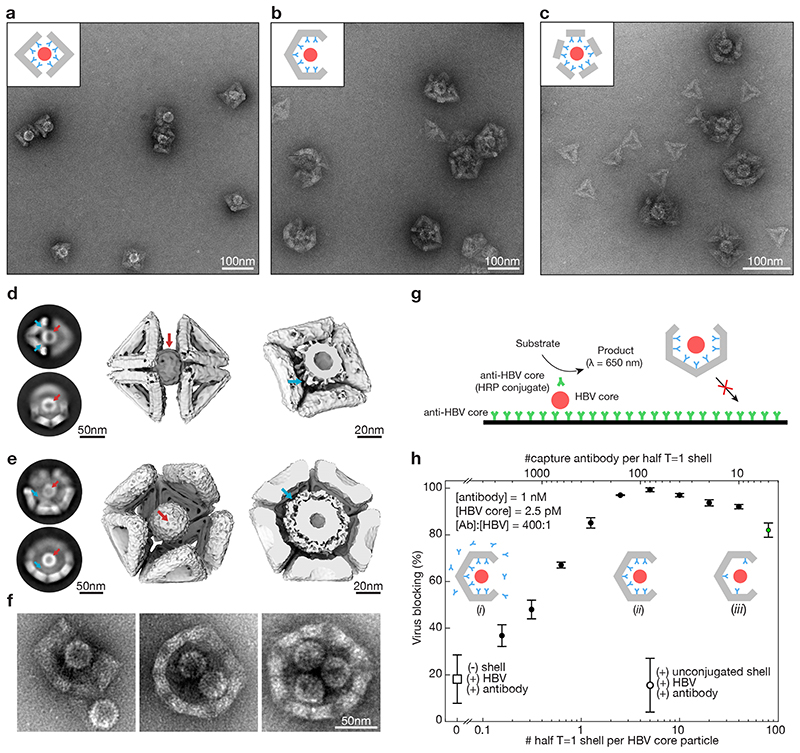
Fig. 5. Trapping of hepatitis B virus (HBV) core particles.
(a) Negative stain TEM images of HBV core particles trapped in octahedral half-shells. Inset: schematic representation of two octahedral half-shells (grey) equipped with antibodies (cyan) with a trapped HBV core particle (red). (b) Same as in (A) with half T=1 shells. (c)) Same as in (A) with monomeric T=1 triangles modified with nine antibodies self-assembled around HBV core particles. (d) Left: Two-dimensional EM class-averages. Middle: Cryo-EM reconstruction of two octahedral half-shells coordinating a trapped hepatitis-B virus particle. See Supplementary Video 6,7. Right: Cut through the cryo-EM map with the HBV core particle trapped. The density around the HBV core particle stems from the antibodies connecting the HBV core particles to the octahedral shell. Red arrows: HBV core particle. Cyan arrows: antibodies connecting the shell to the HBV core particle. (e) Same as in (d) for the T=1 half-shell. The electron density thresholds differ, which makes the HBV core particle look thicker in the T=1 half-shell compared to the half octahedron (right). (f) Negative stain TEM images of T=1 shells with a missing pentagon vertex engulfing up to three HBV core particles. (g) Schematic representation of the in vitro virus blocking ELISA experiment. (h) In vitro virus blocking ELISA experiments. All experiments are done at a ratio of antibody (Ab) to HBV of 400:1. The half-shells have 90 antibody binding sites. Solid filled dots indicate 2.5 pM HBV core particles incubated with pre-assembled mixtures of 1 nM oligonucleotide-conjugated capture antibody and various concentrations of half T=1 shells. Insets: (i) low half-shell concentration for which antibodies saturate the half-shell binding sites and excess antibodies are in solution. (ii) half-shells are saturated with antibody with little antibody remaining in solution. (iii) high half-shell concentration for which antibodies are not saturating all half-shell binding sites. Controls: the open dot represents a mixture of HBV core particles, antibodies and unfunctionalized T=1 half-shells; the open square represents HBV plus antibody without half-shells. The green dot shows a blocking efficiency of about 80% at only a 5:1 ratio of Ab:half-shells. Data is presented as mean ± s.d., n = 3 independent measurements.