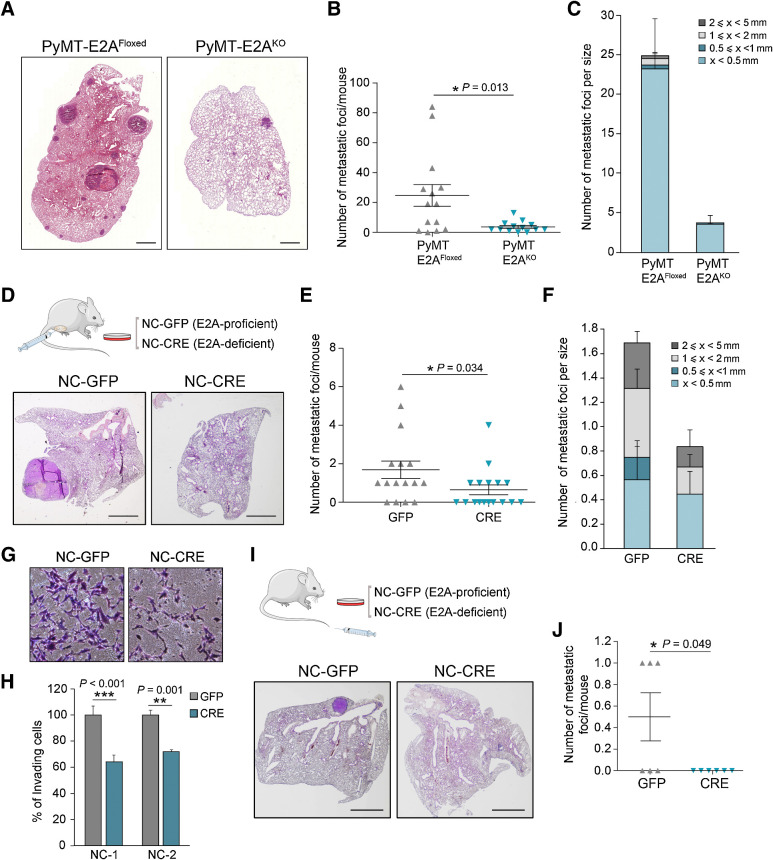
Figure 4.
E2A proteins regulate the metastatic potential of PyMT-derived tumor cells. A, Representative hematoxylin and eosin–stained lung sections showing metastatic lesions from 16-week-old PyMT-E2AFloxed and PyMT-E2AKO mice. Scale bar, 1 mm. B and C, Quantification of the number per mouse (B) and number per size category (C) of lung metastatic foci developed by PyMT-E2AFloxed (n = 14) and PyMT-E2AKO (n = 13) mice at 16 weeks of age. Midlines (B) and barplots (C) show the mean values; error bars, SEM. D–F, Hematoxylin and eosin representative images (D), number per mouse (E), and number per size category (F) of lung metastatic foci after orthotopic injection of E2A-proficient (NC-GFP) and E2A-deficient (NC-CRE) cells into the fat pad of immunodeficient mice. Scale bar (D), 2 mm. Midlines (E) and barplots (F) show the mean values; error bars, SEM; n = 16 mice per genotype. G and H, Representative images of invasion assays on Matrigel chambers (G) and their corresponding quantification (H) of NC-GFP or NC-CRE cells. Data are expressed relative to values of NC-GFP cells and represent the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments in two independent PyMT cell lines. I and J, Hematoxylin and eosin representative images (I) and number (J) of lung metastatic foci per mouse after tail vein injection of NC-GFP or NC-CRE cells into immunodeficient mice. Scale bar (I), 2 mm. Midlines (J) represent the mean ± SEM; n = 6 mice per genotype. P value was calculated by two-sided Mann–Whitney U test in B and E and by two-sided unpaired Student t test in H and J. In panels D and I, schematics of the experiments performed are included.