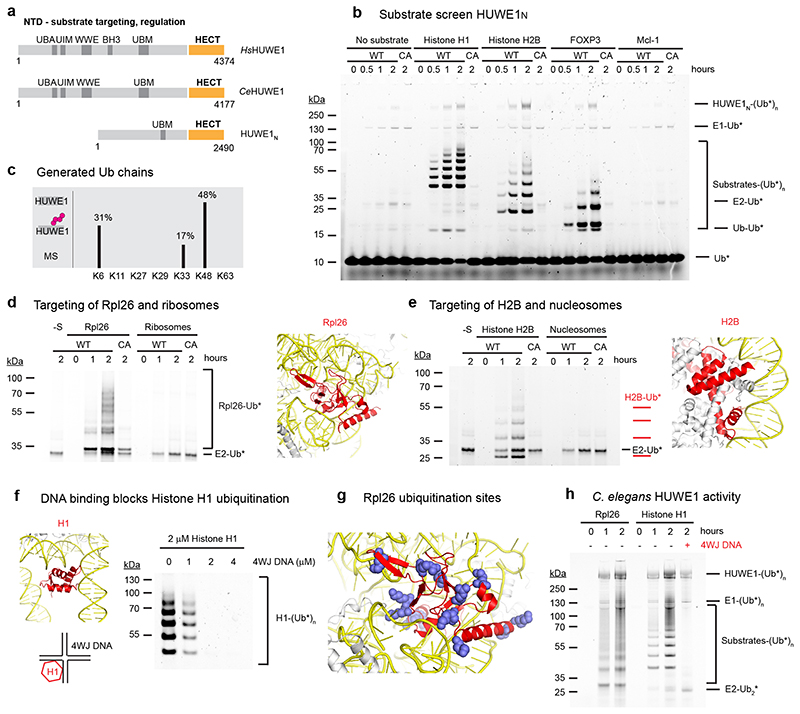
Figure 1. HUWE1N targets orphan proteins for degradation.
(a) Cartoon depicting the domain organization and functional roles of HUWE1. (b) HUWE1N substrate screen. E1-E2-E3 ubiquitination assays were performed using 4 μM of the indicated substrates and either wild-type HUWE1N or the inactive HUWE1N-CA variant. The ubiquitinated products were visualized by using ubiquitin labeled with the DyLight488 fluorophore. (c) Linkage specificity of HUWE1N as seen in autoubiquitination. Ubiquitin chains with the indicated linkage types were detected by mass spectrometry. The ratio of ubiquitinated to total detected peptides for each linkage type is shown as a percentage (d-e) Ubiquitination of an orphan ribosomal subunit and an orphan nucleosome subunit, respectively. Assays were performed with 500 nM substrate and only show the region of the gel containing ubiquitinated substrates, which were visualized with Ub-DyLight800 in (c) and Ub-DyLight488 in (d). The position of Rpl26 (colored red) within the ribosome (PDB 6T59) and histone H2B (colored red) within the nucleosome (PDB 3AFA) are displayed with nucleic acids colored yellow. (f) Histone H1 ubiquitination is blocked by 4WJ DNA. Assays were performed for 120 minutes. (g) An Rpl26 ubiquitination reaction was analyzed by mass spectrometry. Detected ubiquitinated lysines are indicated in the context of the ribosome (PDB 6T59). (h) Ubiquitination of orphan proteins by CeHUWE1, using 2 μM substrate and 4 μM 4WJ DNA in the last lane, and visualized with Ub-DyLight800.