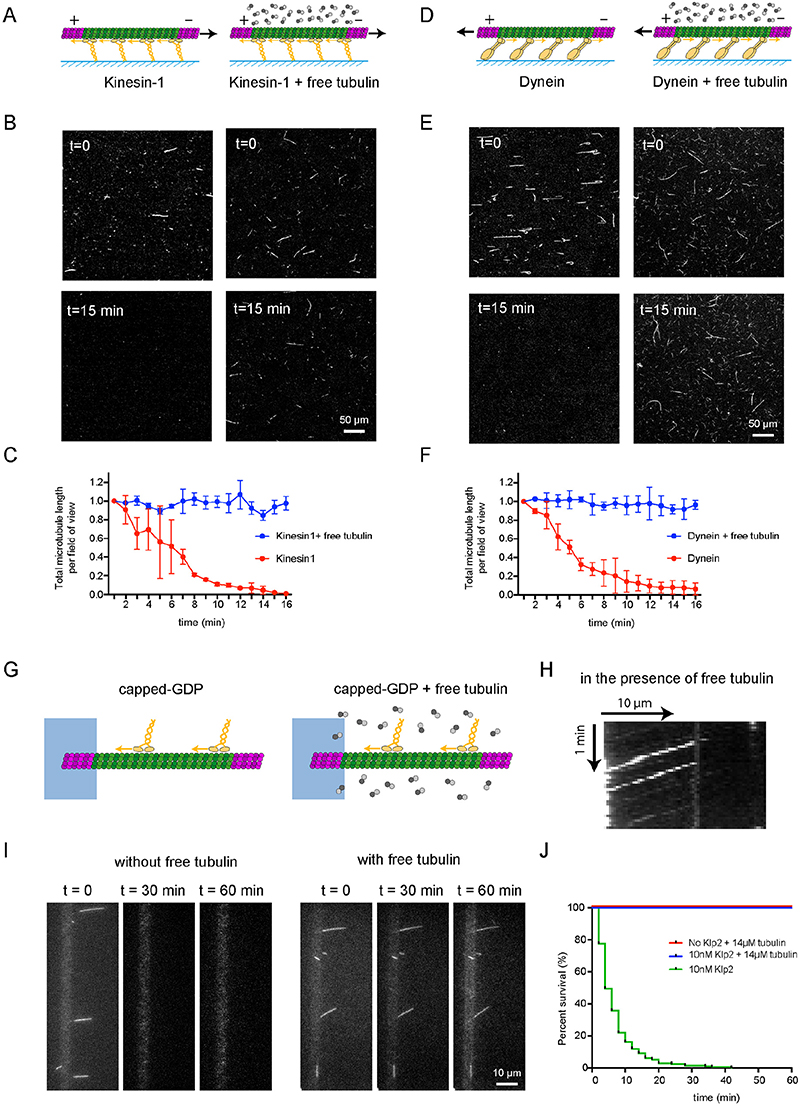
Figure 4. Free tubulin dimers prevent microtubule destruction by kinesin and dynein.
A - Schematic representation of the gliding assay of capped-GDP microtubules on kinesin-1 in the absence (left) or presence (right) of free non-labelled tubulin dimers. B - Images of gliding microtubules when motors are activated by the addition of ATP (t=0, top row) and 15 minutes later (t=15 min, bottom row) in the two conditions described in A. Scale bar: 50 μm.
C - Quantification of microtubule length variations in the experiments shown in B. The microtubule lengths were measured for all microtubules in the 600-μm-wide fields every minute during 15 minutes. Values were normalized with respect to the initial length. Data in the absence of free tubulin dimers are shown in red and correspond to the data shown in figure 1C, those in the presence of 14μM of free dimers are shown in blue. Values were normalized with respect to the initial intensity (Number of independent experiments N=2, without free tubulin n=42, with free tubulin n=74). Scale bar: 50 μm. Error bars represent standard deviation.
D,E,F – Same as A, B and C in the presence of yeast dynein instead of kinesin-1. (N=2, without free tubulin n=24, with free tubulin n=12). Error bars represent standard deviation.
G - Schematic representation of the motility assay in the absence (left) and presence (right) of free non-labelled tubulin dimers.
H - Kymograph showing the position of fluorescent-Klp2 along a microtubule over time. The presence of free dimer did not interfere with the ability of the motor to walk towards microtubule minus ends.
I - Image sequences show microtubules after the addition of Klp2 motors in the absence (left) or presence (right) of 14μM of free tubulin dimers. Images were taken every 2 min. Scale bar: 10 μm.
J - Survival curve of microtubules in the presence of molecular motors and absence of free tubulin (green), in the presence of molecular motors and 14μM of free tubulin dimers (blue) or in the absence of motors and presence of 14μM of free tubulin dimers (red). Data where acquired in the conditions described in I. (N=1; No motor, n=108; 10nM Klp2 with free tubulin, n=70; 10nM Klp2 without free tubulin, n=212).