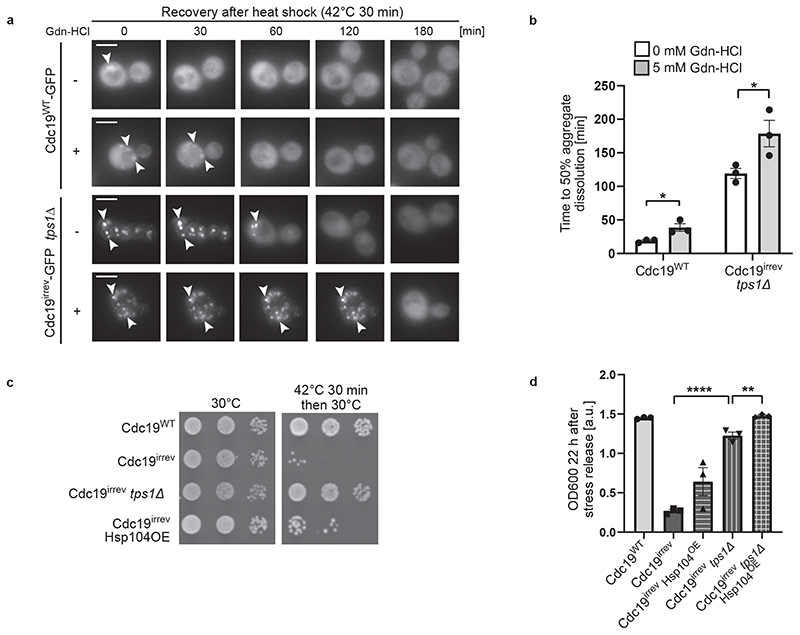
Figure 5. Chaperones are involved in Cdc19 amyloid disassembly.
(A) – (B) Inhibition of Hsp104 activity delays Cdc19 and SG re-solubilization. Cells of the indicated genotype were treated with 5 mM Gdn-HCl for 3 hours prior to a 30 min heat shock at 42 °C. (A) Aggregate disassembly after stress release was monitored by fluorescence microscopy. Representative images, arrowheads indicate Cdc19 aggregates (n = 3 independent experiments). Scale bar: 5 μm. (B) Cdc19 aggregate disassembly was quantified by counting the number of foci at different time points after stress. The average time ± S.E.M. to reach a 50% reduction in foci number is displayed (n = 3 independent experiments, >30 cells per sample per experiment, two-tailed t-test, PWT = 0.0268, Pirrev+tps1Δ = 0.048).
(C) – (D) Overexpression of Hsp104 partially rescues growth of cdc19irrev cells after heat shock. (C) Serial dilutions of exponentially growing cells of the indicated genotype were spotted on agar plates before or after a 30 min heat shock of 42 °C, and imaged after 3 days at 30 °C (n = 3 independent experiments). Where indicated, overexpression of Hsp104 was induced by treating cells with 10 mM estradiol for 3 hours. (D) Growth restart was also quantified by measuring cell density (OD600) over time after inoculation of equal cell numbers at 30 °C. Mean cell density 22 hours after stress release ± S.E.M. is shown (n = 3 independent experiments, two-tailed t-test, Pirrev-irrev+tps1Δ = 0.0000413, Pirrev+tps1Δ - irrev+tps1Δ+Hsp104OE = 0.0055). Source data for all graphical representations can be found in Source Data Fig. 5.