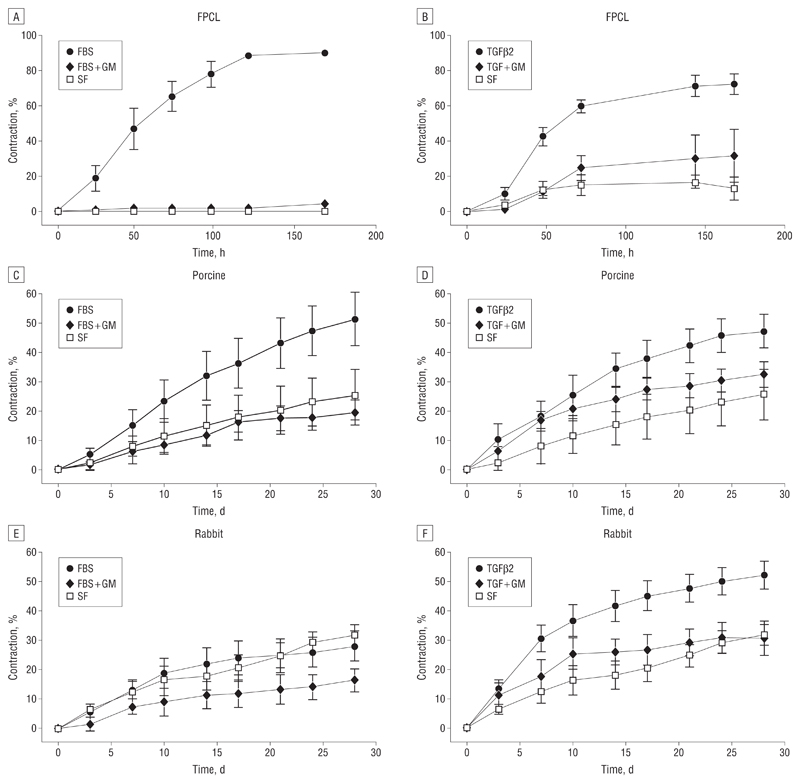
Figure 3.
In vitro and ex vivo contraction analysis. A and B, Fibroblast-populated collagen lattices (FPCL) were used to study contraction by human Tenon fibroblasts. The fetal bovine serum (FBS) induced contraction to approximately 90% of the original gel size and transforming growth factor β2 (TGFβ2) to approximately 75%. In both cases, GM6001 significantly inhibited contraction. C and D, The FBS induced contraction of porcine conjunctiva up to approximately 50% of the original tissue size and TGFβ2 to approximately 45%, and both are inhibited by GM6001. Significant differences between samples in FBS compared with FBS + GM can be seen from day 10 (P<.05), increasing to P<.01 on day 24. Differences between the means of contraction with TGFβ2 and TGF + GM were found to be significant from day 21 (P<.05). E and F, The TGFβ2 increased rabbit conjunctiva contraction to approximately 50%. Differences between the means of contraction with TGFβ2 and TGF + GM were found to be significant from day 14 (P< .05). Gel and tissue areas were expressed as the mean of triplicates, and data are expressed as the mean (SEM) of 5 independent experiments.