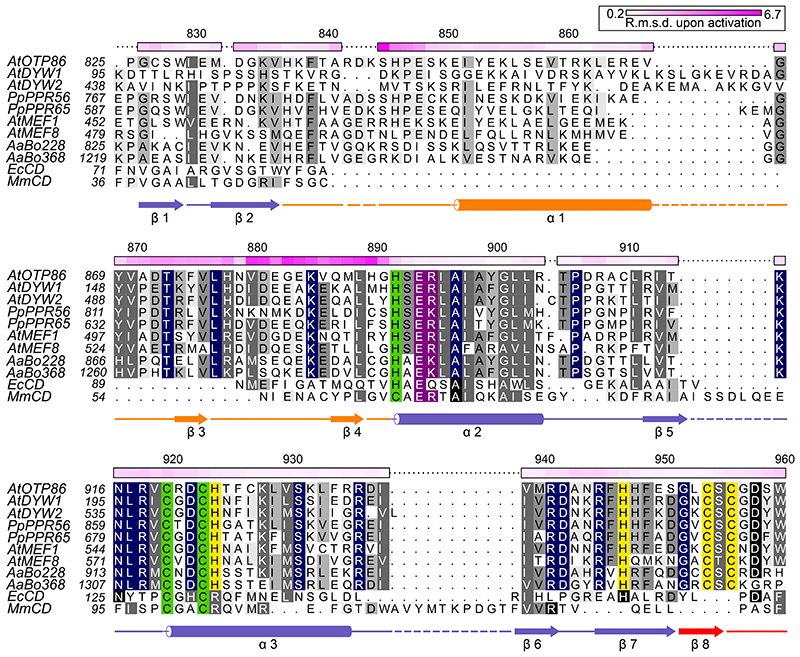
Fig. 2. Structure-based sequence alignment of OTP86DYW.
The alignment compares OTP86DYW with plant organellar DYW domains, hornwort putative U-to-C aminases53,72, C-to-U deaminases from E. coli (EcCD, PDB-ID: 1AF2; ref. 43), and Mus musculus (MmCD, PDB-ID: 2FR6; ref. 44). The alignment was prepared by Chimera employing Clustal Omega and shaded with ALSCRIPT73,74. Proteins are identified on the left of the aligned sequences with residues numbered (see Supplementary Table 2). Higher conservation is indicated by a darker background. Full conservation within DYW domains is indicated by dark blue background shading. Single-residue Cα r.m.s.d. values (calculated with CCP4i) between OTP86DYW and OTP86DYW★ (or structural changes upon activation) are displayed on the top of each alignment block as a colour gradient from white to pink (prepared with Python Matplotlib) and are quantified in the top-right box. The overall r.m.s.d. between the two structures was 1.99 Å, the gating domain residues 870–891 (β-finger) amounted to 2.98 Å. The numbering on top of each block refers to A. thaliana OTP86. Below the alignment blocks, secondary structure elements (α–α-helix, β-β-sheet) of OTP86DYW are shown in slate for the deaminase domain, orange for the gating domain and red for the DYW motif. A dashed line or no line indicates residues missing from the structure or the expression construct, respectively. Green shading indicates residues coordinating the catalytic Zn1 ion; yellow shading indicates residues coordinating the Zn2 atom within the DYW motif and strand β7/helix α3; and purple shading indicates residues relevant for catalysis according to past studies. At, Arabidopsis thaliana; Pp, Physcomitrium patens; Aa, Anthoceros agrestis.