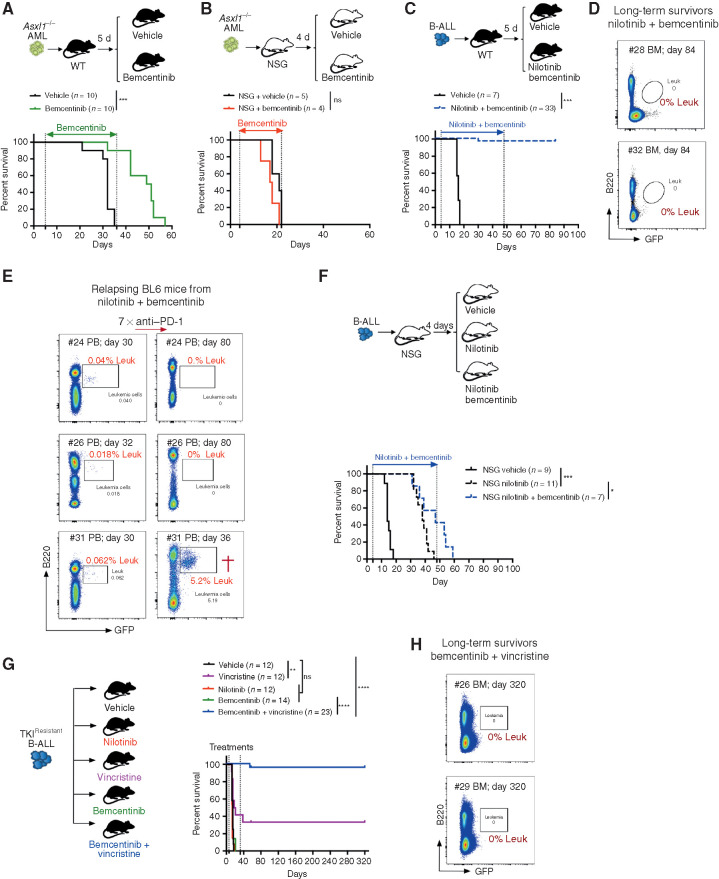
Figure 7.
Systemic AXL inhibition induces potent antileukemic immunity and eliminates leukemic blasts in AXL-negative leukemias. A and B, Kaplan–Meier survival curves of C57BL/6 WT mice (A) or NSG mice (B) challenged with 5.105Asxl1−/− AML cells and treated with either vehicle or bemcentinib (50 mg/kg, twice daily). ns, not significant. ***, P < 0.001, log-rank (Mantel–Cox) test. C, Kaplan–Meier survival analysis of C57BL/6 WT mice challenged with 103 B-ALL cells and treated with either vehicle (n = 7) or nilotinib (80 mg/kg, once a day) plus bemcentinib (50 mg/kg, twice daily; n = 33) for a total of 44 days. Data are pooled from two independent experiments. ***, P < 0.001, log-rank (Mantel–Cox) test. D, Representative FACS plots depicting absence of GFP+ B220dim leukemic cells in the bone marrow of long-term survivors from C. E, Mice from C were followed by weekly bleeding. Three of 33 mice (#24, #26, and #31) showed GFP+ cells indicative of disease recurrence and were subjected to anti–PD-1 treatment as indicated (7 × 200 μg/mL every fourth day). Mouse #31 succumbed to full-blown leukemia on day 36, while #24 and #26 remained leukemia-free. F, Kaplan–Meier survival analysis of NSG mice challenged with 103 B-ALL cells and treated with either vehicle, nilotinib, or nilotinib plus bemcentinib for a total of 44 days as in C. ns, not significant, log-rank (Mantel–Cox) test. G, WT mice were injected with 103 TKIR B-ALL cells. After 5 days, mice were randomly attributed to the indicated vehicle or treatment groups and their survival depicted using a Kaplan–Meier analysis. Data are pooled from two independent experiments. ns, not significant, **, P < 0.01; ****, P < 0.0001, log-rank (Mantel–Cox) test. H, Representative FACS plots depicting absence of GFP+ B220dim leukemic cells in the bone marrow of bemcentinib + vincristine–treated long-term survivors from G. In all experiments, treatments were initiated and stopped on the days indicated by dotted lines.