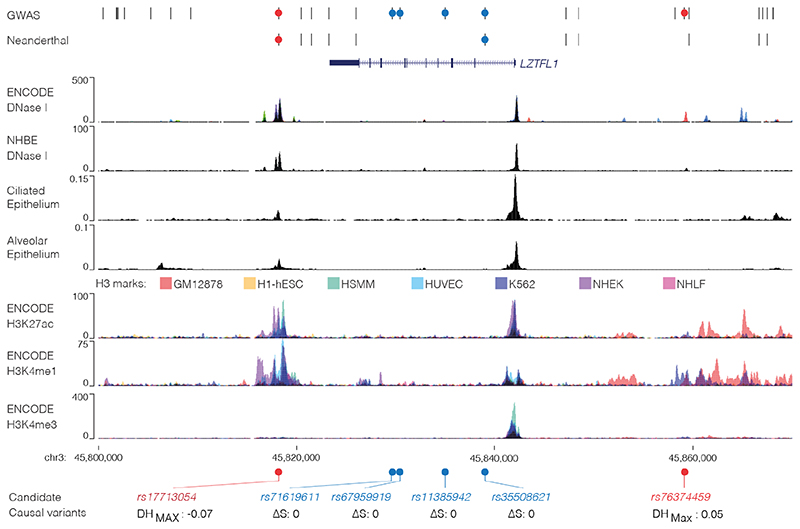
Figure 1. Identification of a potentially causative COVID-19 risk variant.
COVID-19 risk variants from GWAS were assessed for multiple mechanisms. All genome-wide significant variants and linked variants are shown (GWAS) as are variants present in the Vindija Neanderthal12 risk haplotype. Circles indicate variants assessed for splicing changes (blue circles, SpliceAI18: ΔS score [0-1, where 1 is most damaging]), and presence in cis-regulatory elements using open chromatin in 95 ENCODE overlaid DNase I datasets (red circles), normal human bronchial epithelial cells (NHBE), and single-cell ATAC-seq from fetal ciliated epithelium and alveolar epithelium34. Histone H3 modification tracks show presence of marks associated with active transcription (H3K27ac) at enhancers (H3K4me1) and promoters (H3K4me3). Variants in open chromatin are given deepHaem damage scores (DH, 0-1) with sign indicating increased (-) or decreased (+) accessibility. Region shown is chr3:45,800,000-45,870,000, hg38.