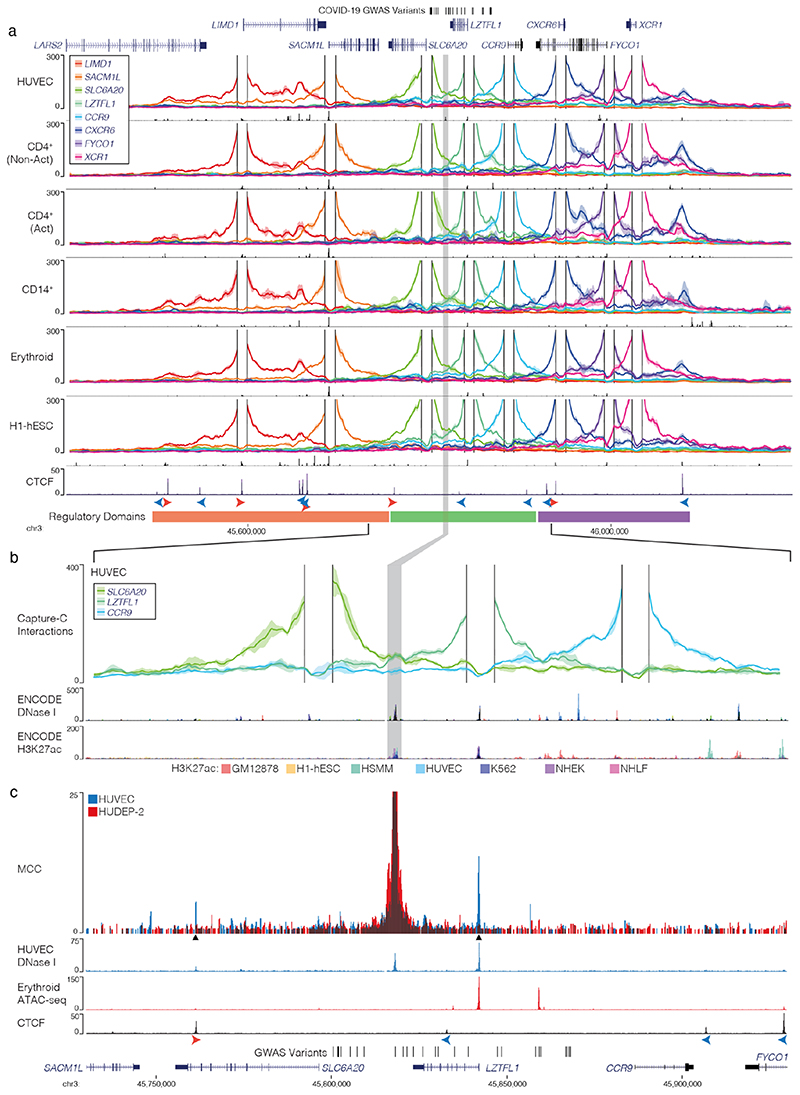
Figure 3. The interaction landscape of the severe COVID-19 risk locus.
a, DpnII Capture-C derived mean interaction count (n = 3 for all except CD14+: n = 2) and one standard deviation (shading) for gene promoters in human vein endothelial cells (HUVEC), resting and activated T-Cells (CD4+ Non-Act/Act), monocytes (CD14+), CD235+ CD71+ erythroid cells and human embryonic stem cells (H1-hESCs). The enhancer containing rs17713054 is highlighted by a grey box. ATAC-seq/DNase I for each cell-type is shown underneath in black. CTCF track shows binding of the CCAAT-binding factor which acts as a boundary with forward and reverse motif orientation shown with arrowheads (red and blue respectively). Three broad regulatory domains were identified as regions with overlapping interactions. Region: chr3:45,400,000-46,200,000, hg38. Per fragment interactions were smoothed using 400-bp bins and an 8-kb window. b, The rs17713054 regulatory domain in endothelial cells (HUVEC). Overlaid DNase I shows accessible sites in 95 cell types and H3K27ac shows active elements. Region: chr3:45,730,000-45,930,000, hg38. Per fragment interactions were smoothed using 250-bp bins and a 5-kb window. Solid line shows mean interaction count (n = 3 independent samples) with one standard deviation (shading). c, Micro Capture-C (MCC) of the rs17713054 enhancer in endothelial (HUVEC, blue) and erythroid (HUDEP-2, red) cells with tissue specific open chromatin tracks (n = 3). Peak analysis of MCC using LanceOtron to compare HUVEC and HUDEP-2 profiles identified two significantly enriched peaks in HUVEC cells (black triangles, P ≤ 1 × 10-999) which correspond to the LZTFL1 promoter and the upstream CTCF site.