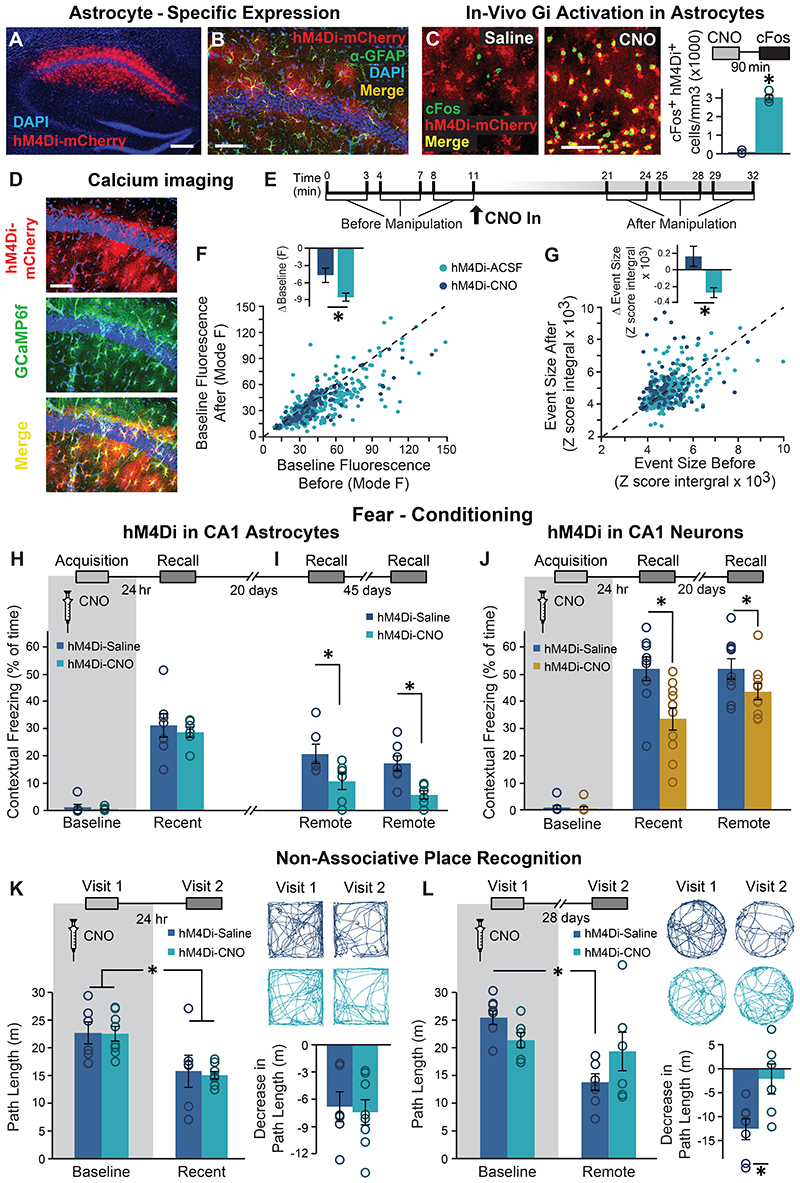
Figure 1. Astrocytic Gi pathway activation in CA1 during learning specifically impaired remote contextual memory.
(A) Bilateral double injection of AAV8-GFAP∷hM4Di-mCherry resulted in hM4Di expression selectively in CA1 (scale bar 200μm). (B) hM4Di (red) was expressed in the astrocytic membrane around the soma, as well as in the distal processes (scale bar 50μm). (C) CNO administration in-vivo to mice expressing hM4Di (red) in CA1 astrocytes resulted in a significant increase in cFos expression (green) in these astrocytes, compared to Saline injected controls (p<0.00005, n = 2-4 mice, 6-15 slices per groups; scale bar 50μm). (D) hM4Di-mCherry and GCaMP6f were co-expressed in CA1 astrocytes. (E) Astrocytes were imaged for 3x3min before and after application of ACSF (109 ROIs from 5 mice) or CNO (10μM; 299 ROIs from 8 mice). CNO application triggered a decrease in baseline intracellular Ca2+ levels, reflected by the mode of fluorescence levels (p<0.01)(F) and reduced the total size of Ca2+ events in these cells (p<0.005)(G), compared to astrocytes treated with ACSF. All ROIs are presented as dots in a scatter plot, and the average change (Δ) following treatment is plotted in the insert. (H) Mice expressing hM4Di in their CA1 astrocytes were injected with either Saline (n=7) or CNO (n=6) 30min before fear conditioning (FC) acquisition. CNO application before training had no effect on baseline freezing before shock administration or on recent contextual freezing on the next day compared to Saline treated controls. (I) CNO application before training resulted in a >50% impairment (p<0.05) in contextual freezing in CNO-treated mice tested 20 days later, compared to Saline treated controls (left). An even bigger impairment of >68% (p<0.005) was observed 45 days later (right). (J) Mice expressing hM4Di in their CA1 neurons were injected with either Saline (n=9) or CNO (n=10) 30min before FC acquisition. CNO application before training had no effect on baseline freezing before shock administration, bur resulted in decreased recent contextual freezing on the next day (p<0.005), and decreased remote recall 20 days after that (p<0.05) compared to Saline treated controls. (K) In the non-associative place recognition test, astrocytic Gi pathway activation by CNO application before a first visit to a new environment had no effect on recent memory, reflected by a similar decrease (p<0.0001) in the exploration between Saline injected (n=6) and CNO-treated mice (n=8). Example exploration traces andthe average change (Δ) in exploration following treatment are shown on the right. (L) Astrocytic modulation impaired remote recognition of the environment on the second visit, reflected by a decrease in the exploration only in the Saline injected (n=7)(p<0.01), but not CNO-treated (n=6) mice. Example exploration traces and average decrease Δ are shown on the right. Data presented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM).