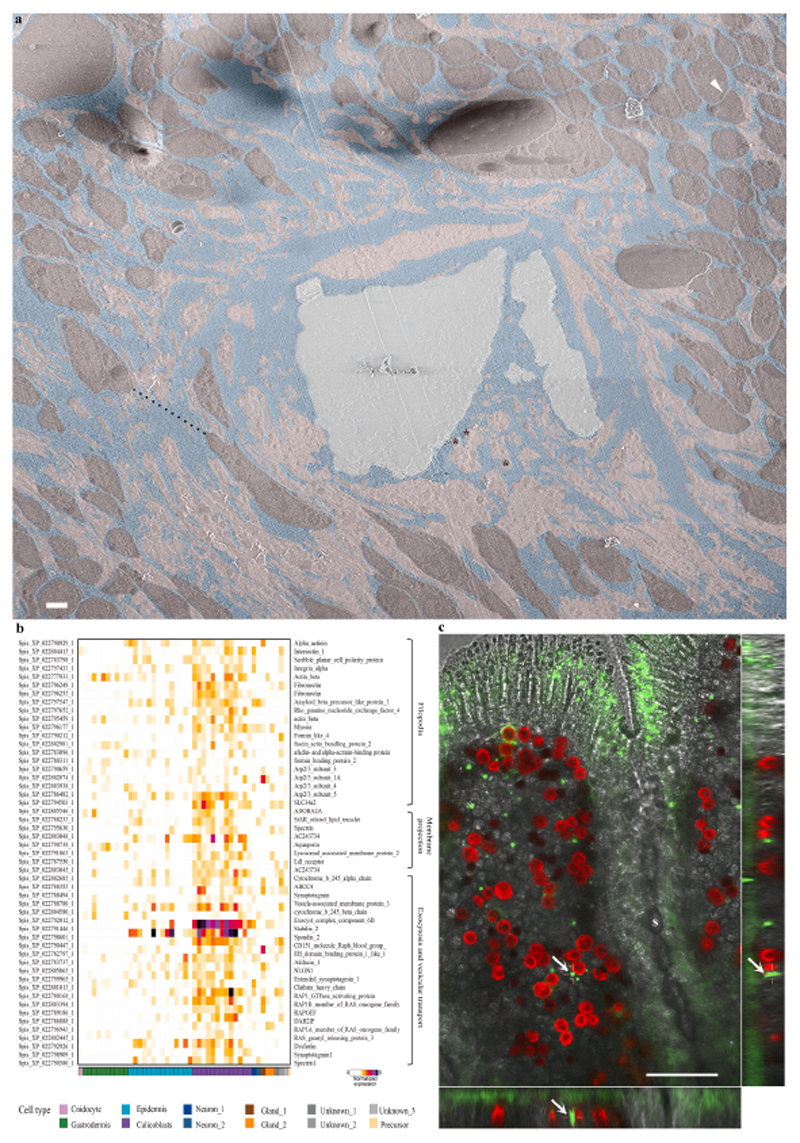
Fig. 6. The paracellular space in primary polyps.
(a) An overview image stitched from several high magnification cryo-SEM micrographs of the calicoblastic tissue around a septum in a cryo-planed primary polyp (same area as pointed with a white arrow in Fig. 5a. Tightly packed calicoblastic cells with a paracellular spacing of 30 nm are pointed with a white arrowhead (top right corner). Dispersed cell packing with a paracellular space of 8.4 μm is denoted with a black dashed line. Calicoblastic cell bodies are highlighted with pseudo–burgundy, filopodia in pseudo–pink, ECM in pseudo–blue, and the mineral in pseudo–grey. Three representative vesicles contained within the filopodia network are marked with black asterisks. Scale bar is 2 μm. (b) Gene expression heatmap for selected genes involved in filopodia structure and function, membrane projections, exocytosis, and vesicular transport across all cell types of S. pistillata primary polyp (all selected genes are highly expressed in the calicoblasts cells -purple). (c) In-vivo confocal laser scanning fluorescence image of the coral tissue around a septum (s) in a primary polyp labeled with green-fluorescent beads of 1 μm diameter. Green-fluorescent beads, red-symbionts auto-fluorescence, grey scale-transmitted laser scanning image. The center large panel is one horizontal (xy) plane taken 16 μm above the glass, roughly in the middle of the z-stack data set covering the entire sample thickness (30 μm). The right and bottom panels are two side views of the z-stack data set (i.e. xz, and yz) showing fluorescent beads incorporated inside the coral tissue. One representative green-fluorescent bead is depicted with a white arrow in all three panels.