Figure 4.
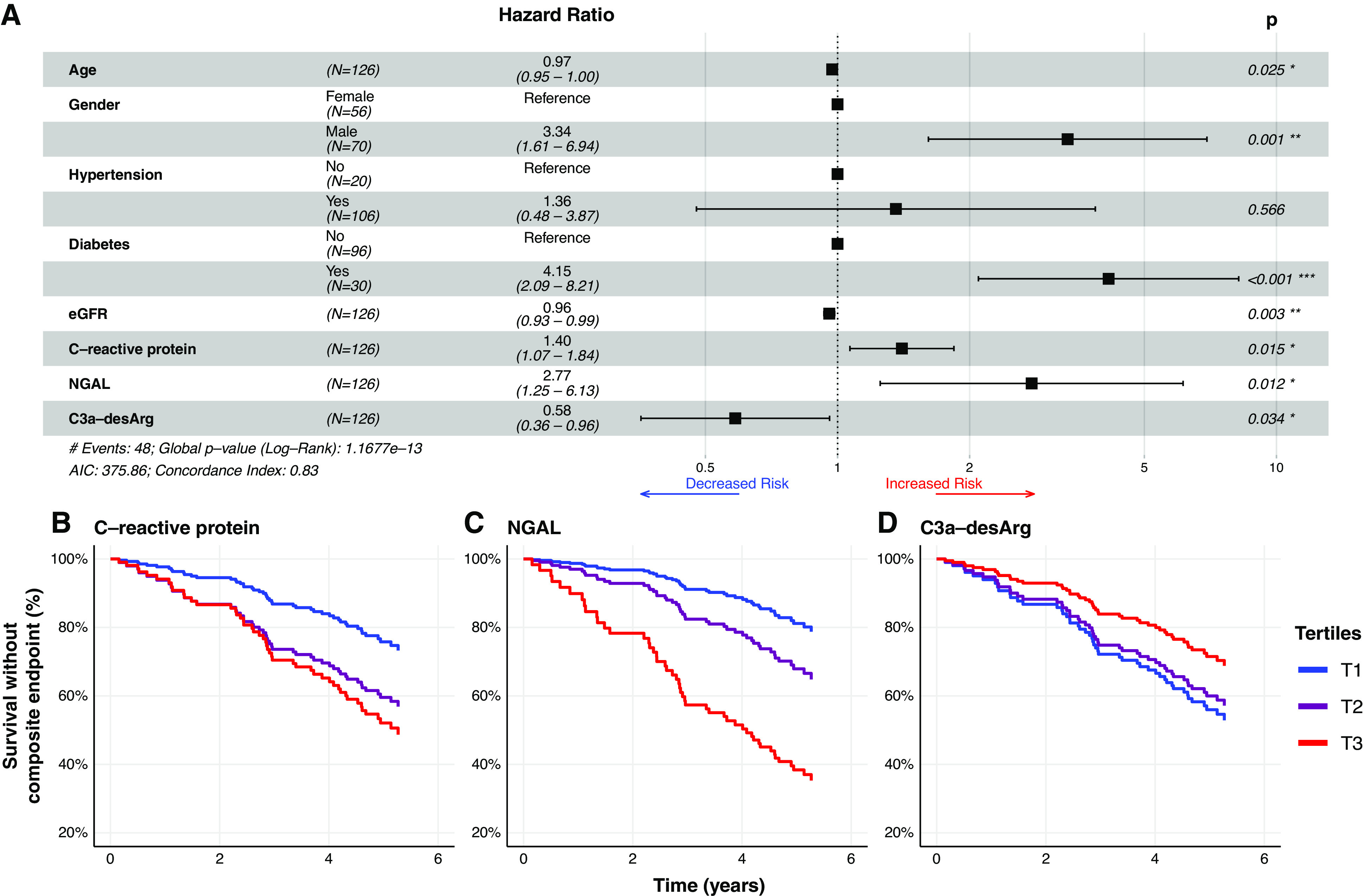
C-reactive protein, NGAL, and C3a-desArg independently predict time to development of a composite renal and mortality end point (Cox proportional hazards regression). (A) Forest plot of parsimonious Cox proportional hazards regression model incorporating clinical variables and serum biomarkers predictive of a composite renal and mortality end point (n=126). C-reactive protein (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.4; 95% 95% CI, 1.1 to 1.9) and NGAL (aHR, 2.7; 95% CI, 1.3 to 5.8) were positively associated with time to the composite renal and mortality end point. C3a-desArg values were inversely associated with time to the composite renal and mortality end point (aHR, 0.5; 95% CI, 0.3 to 0.9). (B–D) Plots of survival without the composite renal and mortality end point derived from the fully adjusted, multivariate clinical plus biomarker Cox proportional hazards regression model presented in the forest plot in (A), stratified by tertiles of serum (B) C-reactive protein, (C) NGAL, and (D) C3a-desArg. Biomarker values were log transformed for modeling. Hazard ratios from Cox models are expressed per one unit change in natural logarithm biomarker concentrations. Composite renal and mortality end point: ≥40% decrease in Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration eGFR, doubling of serum creatinine, RRT, or mortality. AIC, Akaike information criterion. T1, tertile 1. *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001
