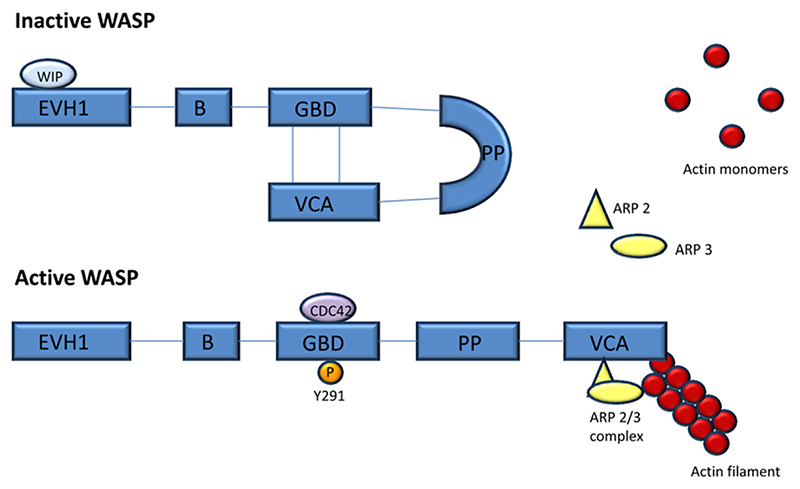
Figure 1.
Domain structure of WASP in its inactive and active forms. At rest, WASP exists in an autoinhibited state where the VCA region associates with the GBD region, the conformation of which is stabilised by WIP. WASP becomes activated through binding partners such as the GTPase CDC42 or phosphorylation of a tyrosine residue (Y291), which release the VCA domain and expose the ARP 2/3 binding domain. The ARP 2/3 complex recruits actin monomers resulting in the formation of branched actin filaments. ARP 2/3, actin-related protein; B, basic domain; CDC42, cell division cycle 42; EVH1, Ena-VASP homology domain; GBD, guanosine triphosphate binding domain; P, phosphate; PP, polyproline domain; VCA, verprolin homology/central/acidic domain; WASP, Wiskott Aldrich syndrome protein; WIP, WASP interacting protein.