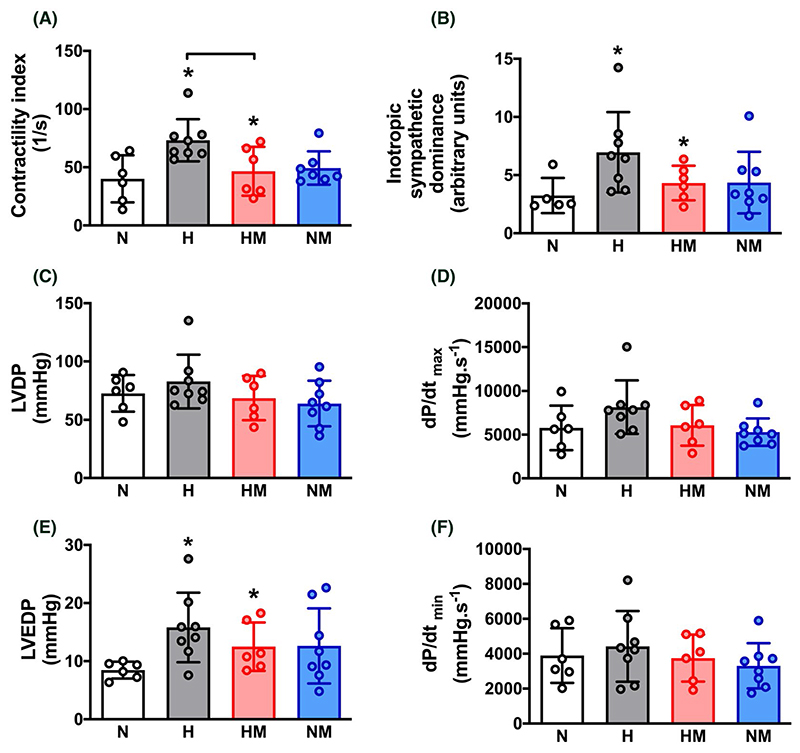
Figure 4.
Effect of hypoxic pregnancy and MitoQ on isolated cardiac function in the adult offspring. Values are means ± SEM. for the contractility index (A), the inotropic sympathetic dominance (B), left ventricular developed pressure (LVDP; C), the maximum first derivative of the left ventricular pressure (dP/dtmax; D), left ventricular end diastolic pressure (LVEDP; E), and the minimum first derivative of the left ventricular pressure (dP/dtmin; F) in adult offspring of normoxic (N, n = 5-6), hypoxic (H, n = 8), hypoxic treated with MitoQ (HM, n = 6), or normoxic treated with MitoQ (NM, n = 7-8) pregnancies. The inotropic sympathetic dominance was calculated as the ratio of the LVDP response to a maximal dose of isoprenaline relative to a maximal dose of carbachol. Statistical differences are (P < .05): * main effect of hypoxia; hypoxia x MitoQ interaction indicated by brackets (Two-Way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc comparison)