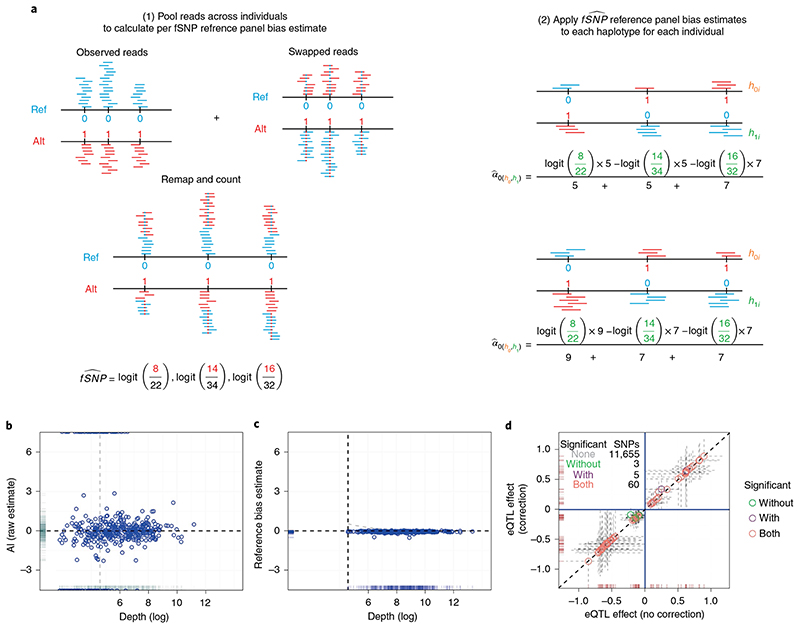
Fig. 2. Reference mapping bias correction.
a, Schematic representation of BaseQTL correction for reference panel bias. For each read that maps to an fSNP, we create a new read in which the allele of the fSNP is swapped (represented as a blue dot in a red read (alt–> ref) or a red dot in a blue read (ref->alt). The pooled reads, which have a 50:50 ratio of reads carrying the reference (ref) or alternative (alt) alleles at each fSNP, are remapped, and the number of reads mapping to each allele stored. b, For each fSNP we calculated the proportion of reads overlapping the alternative allele across all heterozygous individuals, which we refer to as the raw estimate of allelic imbalance. The plot shows logit-transformed raw estimates for AI (y axis) against depth (x axis) for each fSNP. The horizontal line indicates no allelic imbalance, the gray vertical line is displayed to ease comparison with c. c, Same as b but the y axis corresponds to the logit allelic imbalance (AI) estimates obtained as described in a. The vertical line indicates the read threshold selected for including estimates for inference (100 reads across all samples). d, each symbol corresponds to a gene–SNP association comparing the eQTL estimates (log2 allelic fold change) obtained with or without applying our reference bias panel correction.