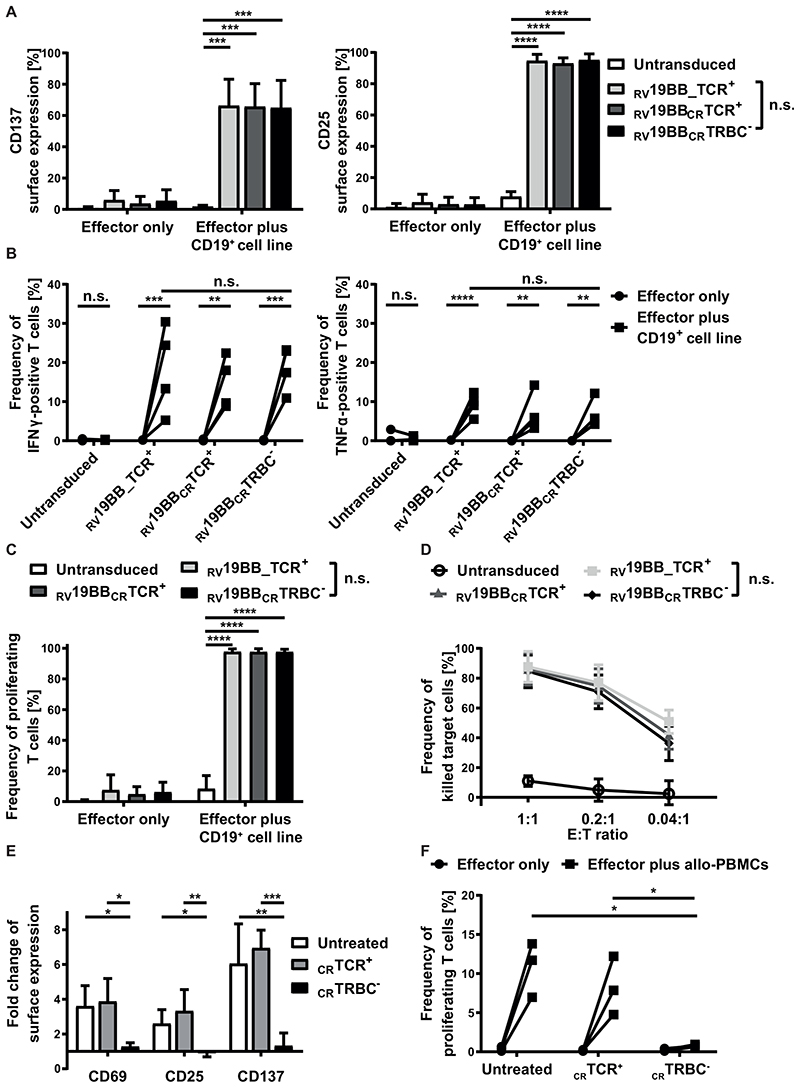
Fig. 3. Functionality of RV19BBCRTRBC-CAR-T cells and alloreactive potential of TCR+ T cells in vitro.
(A-D) The functionality of RV19BBCRTRBC-CAR-T cells was compared to RV19BB_TCR+, RV19BBCRTCR+CARs and untransduced T cells (UTs) in different functionality assays. (A) 24 hours after co-culturing the CAR-T cells with CD19+ target cells in a 1:1 E:T ratio the cells were harvested and analyzed for expression of activation markers CD137 and CD25 (n=6). (B) Intracellular staining of IFNγ and TNFα was performed after 24 hours of co-culturing effector cells with CD19+ cells at an E:T of 1:1 (n=4). (C) CFSE labeled T cells were used to analyze the frequency of proliferating effector cells after contact with CD19+ target cells for 72 hours (n=3). (D) CD19+ target-cell killing was determined by flow cytometry after target cells were co-cultured for 48 hours with CAR-T cells in different E:T ratios (n=4). (E,F) Untransduced, CRTCR+, CRTRBC- T cells were co-cultured with allogeneic PBMCs (allo-PBMCs) pooled from six different donors and co-cultured at an E:T ratio of 1:5. (E) After 48 hours of co-culture, T cells were analyzed for surface expression of the activation markers CD69, CD25 and CD137 (n=3). (F) Percentage of proliferating T cells after contact with allogeneic PBMCs was analyzed after five days (n=3). A two-tailed paired t test or one-way ANOVA was performed to determine statistical significance. RV19BB_TCR+=conventional CAR-T cells without electroporation, RV19BBCRTCR+=CAR-T cells electroporated with nonsense gRNA, RV19BBCRTRBC-=CAR-T cells electroporated with TRBC-targeting gRNA, n.s.=not significant, E:T ratio=effector to target ratio.