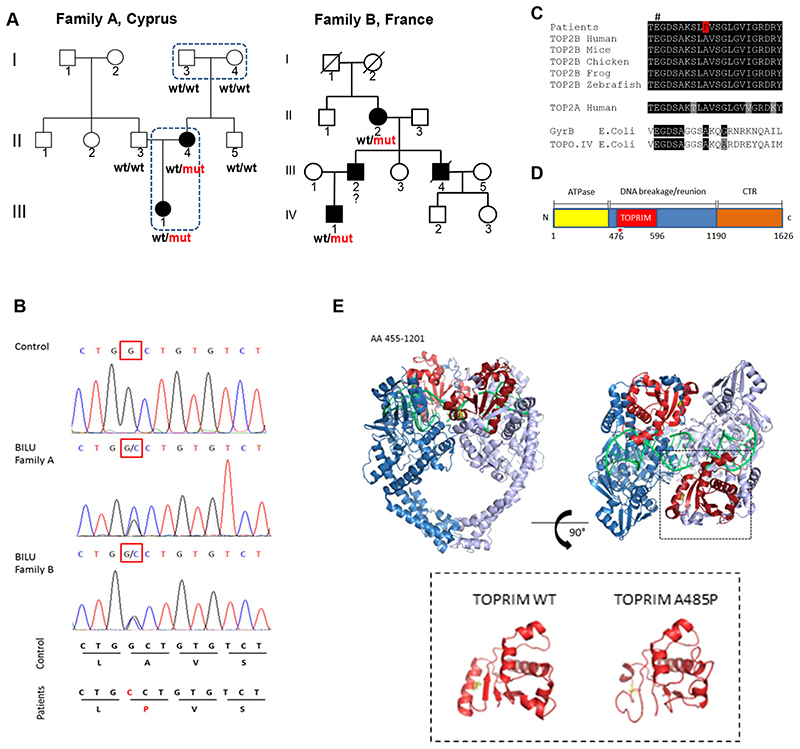
Figure 1. Novel dominant mutation A485P affects TOP2B catalytic site and causes the BILU syndrome.
(A) Two families with the BILU syndrome: ○ and □-unaffected, ● and ■-affected; wt-wild-type allele, mut - A485P mutation in TOP2B. Exome sequencing was performed in four subjects shown by dotted lines. (B) Electrophoregrams of the TOP2B genomic DNA sequence showing the same mutation in patients from the two BILU families. (C) Multispecies protein sequence alignment of type II topoisomerases. # indicates a conserved glutamate essential for TOP2B activity. (D) Schematic representation of domains of the TOP2B protein. The A485P mutation in the TOPRIM domain is shown by a red star. The TOPRIM domain is part of the DNA gate that catalyzes DNA cleavage and re-ligation. (E) Structure of the TOP2B homodimer (amino acid residues 455-1201) in complex with DNA (green); the TOPRIM domain (red) and the alanine at codon 485 (yellow) (upper panel). I-TASSER-modeled structures of the TOP2B TOPRIM domain; WT – wild-type (lower panel).