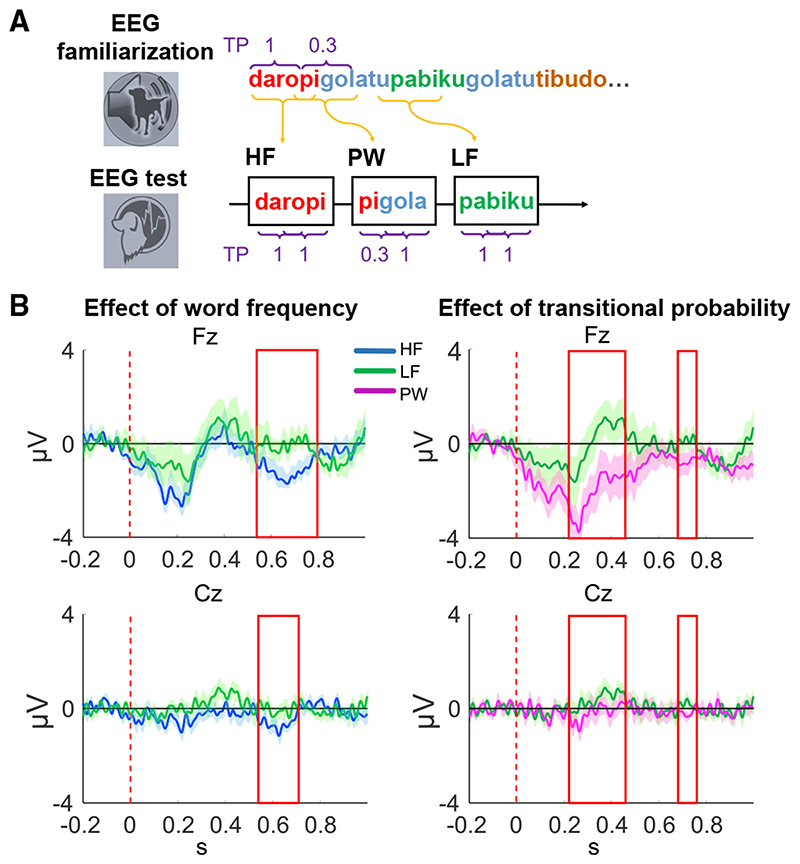
Figure 1. Experimental procedures and results of the EEG experiment.
(A) Sessions in the EEG experiment. Top row: familiarization phase is shown. Dogs listened for ca. 8.5 min to a continuous speech stream consisting of a set of 12 syllables forming four artificial words, which followed each other in a random order. Bottom row: test phase is shown. Three conditions were created from the stimuli of the familiarization phase, which were then played back in isolation: high word frequency, high transitional probability words (HF); low word frequency, high transitional probability words (LF); and low word frequency, low transitional probability words (partwords [PW]). TP, transitional probability.
(B) Significant ERP effects of the sliding time window analysis at the Fz and Cz electrodes in the test phase. The effect of word frequency (i.e., frequency of syllable co-occurrence) was obtained by contrasting HF words with LF words. The effect of transitional probability was obtained by contrasting LF words with PWs. Vertical dashed line shows the timing of word onset (0 s), the red rectangle represents the significant time windows where condition differences were found, and shadows represent SEM.
See also Figures S1 and S2 and Tables S1 and S5.