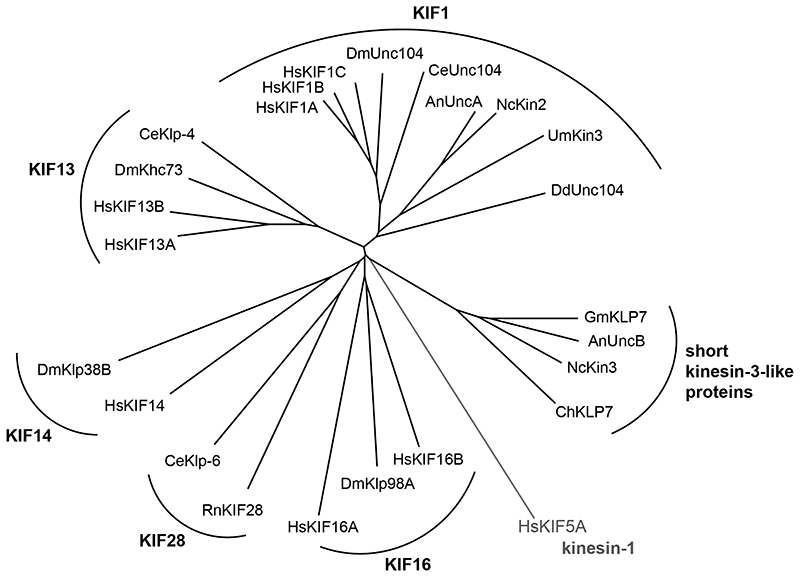
Fig. 1. Kinesin-3 tree.
Phylogenetic tree of all kinesin-3 family members from Homo sapiens (Hs), Drosophila melanogaster (Dm), Caenorhabditis elegans (Ce), Ustilago maydis (Um), Aspergillus nidulans (An), Neurospora crassa (Nc), and Dictyostelium discoideum (Dd). Selected kinesin-3 members from Rattus norvegicus (Rn), Gibberella moniliformis (Gm), and Cochliobolus heterostrophus (Ch) are also shown. Subfamilies are indicated in bold font. Human KIF5A, a kinesin-1, was used as root (shown in gray). To calculate tree information in Clustal Omega [130], kinesin motor domain sequences were aligned and cropped to a ~330-bp-long conserved region. The tree information was then used to generate a radial tree using T-REX tree viewer [131].