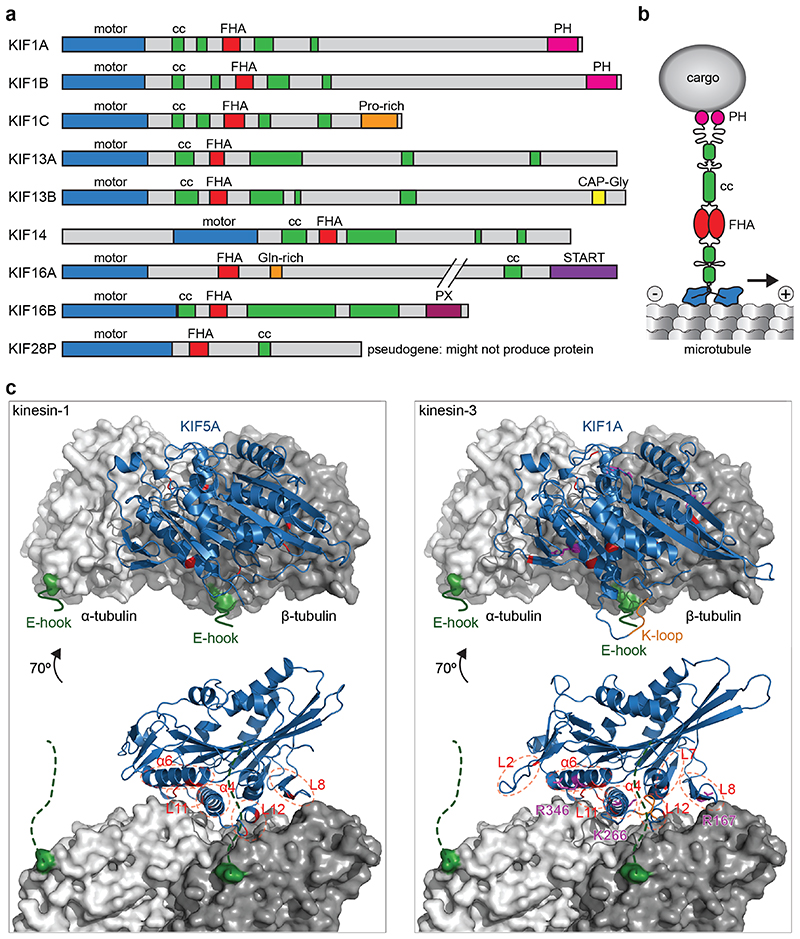
Fig. 2. Structure of kinesin-3 motors.
a) Primary structure of human kinesin-3 members with characteristic N-terminal motor domain, FHA domain, and tail with several short coiled-coil (CC) regions in addition to a variety of protein or lipid interaction motifs. b) Schematic representation of a dimeric kinesin-3 motor and its interaction with the microtubule surface as well as a cargo vesicle. c) Structural model of kinesin motor domains binding to the microtubule (one αβ - tubulin heterodimer shown, in gray). The flexible C-terminal tubulin tails (E-hooks) are indicated in green. Key regions of the kinesin motor domain (blue) that contribute to interaction with microtubules are highlighted in red for both KIF5A, a kinesin-1, and KIF1A, a kinesin-3. Key residues that were shown to contribute to 10-fold higher processivity of kinesin-3 are shown in magenta [53, 54]. PDB accession numbers: 4UXP and 4UXY.