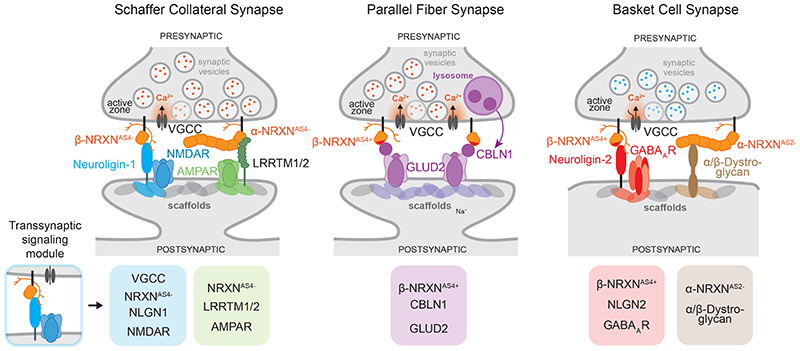
Figure 4. Examples of synaptic interaction modules nucleated by Neurexin proteins.
Simplified model illustrating trans-synaptic interaction modules assembled around presynaptic Neurexin protein isoforms. Amongst other components, CA3-CA1 Schaffer collateral synapses in the mouse hippocampus contain trans-synaptic NRXNAS4--NLGN1 and NRXN-LRRTM complexes which recruit postsynaptic NMDA and AMPA-type glutamate receptors. Note that LRRTM proteins bind α and β Neurexins – but for simplicity only the interaction with α is depicted here. Cerebellar parallel fiber synapses largely rely on a single trans-synaptic module consisting of NRXNAS4+ isoforms, extracellular CBLN1 proteins and the postsynaptic receptor GLUD2. CBLN1 is secreted from lysosome-like carrier vesicles 140 . Note that CBLN1 interacts with α and β Neurexins – but for simplicity only the interaction with β is depicted here. GABAergic basket cell synapses in the mouse hippocampus contain modules of NRXNAS4+ and NRXNAS2- isoforms linking to postsynaptic NLGN2 or α/β Dystroglycan proteins, respectively. Red dots within synaptic vesicles indicate the neurotransmitter glutamate, blue dots represent GABA. One major contribution of Neurexins at synapses is the incorporation of functional voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCC) at synapses, facilitating the calcium-dependent release of synaptic vesicles 19,142,143 . The lower row displays illustrations of individual trans-synaptic modules present at the respective synapses.