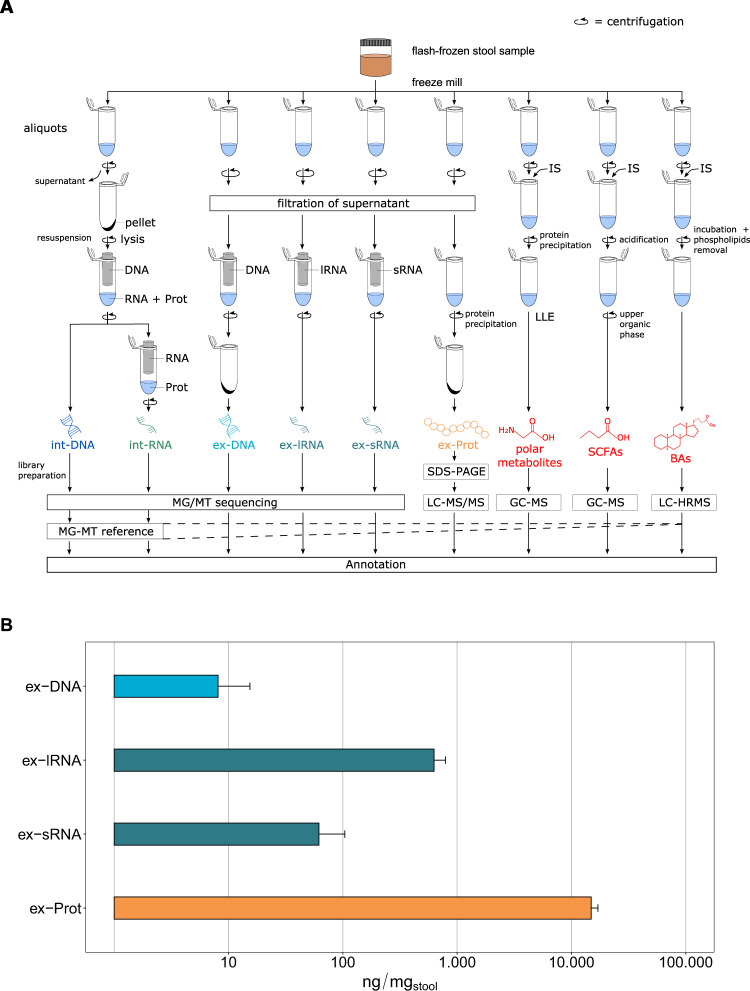
Fig. 1. Overview of the methodological workflow and characteristics of the obtained biomolecular fractions.
A Flowchart of the experimental and bioinformatic analyses. Flash-frozen stool samples are divided into aliquots for subsequent biomolecular extractions. Int-DNA are obtained after elution of the lysate bound onto an AllPrep DNA spin column, the flow-through is loaded onto a RNeasy spin column for int-RNA isolation. To obtain the extracellular fractions, the supernatant is first filtered through a polyethersulfone (PES) membrane. Nucleic acid fractions are isolated using specific columns (NucleoSpin miRNA Plasma kit for ex-DNA and ex-sRNA, NucleoSpin RNA Blood kit for ex-lRNA). Ex-DNAs are subjected to an additional concentration step. All nucleic acid fractions are subjected to high-throughput sequencing. Ex-Prot are obtained from the resulting pellet after protein precipitation and analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by LC-MS/MS. The sequencing information from the intracellular fractions allows for genome reconstruction by a DNA-RNA co-assembly using IMP [10]. This MG-MT reference allows further mapping and annotation of the extracellular fractions. Polar metabolites, SCFAs, and BAs are extracted from their respective aliquots by addition of specific internal standards (IS) and further processing of the supernatant (Supplementary Materials and Methods). The extracts are then analyzed by GC-MS, GC-MS, and LC-HRMS, respectively. B Masses of biomolecules extracted per mg of original stool sample (logarithmic scale). Error bars represent standard deviation on four independent samples. ex-DNA extracellular DNA, ex-sRNA extracellular small RNA, ex-lRNA extracellular large RNA, ex-Prot extracellular proteins, SCFAs short-chain fatty acids, BAs bile acids.