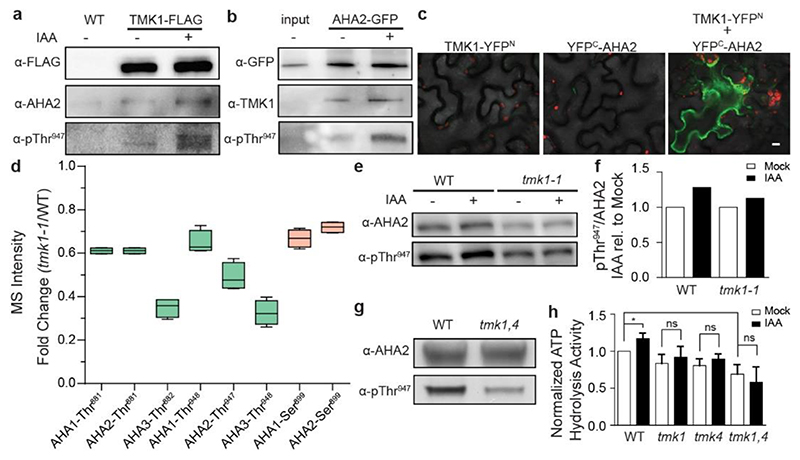
Figure 3. TMK1 directly mediates auxin-induced H+-ATPase activation.
a, Co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP) of the pTMK1::TMK1-FLAG from roots mock or 100 nM IAA-treated for 30 minutes, followed by Western blot detection of AHA2 and Thr947-phosphorylated AHA2. The control is the co-IP of WT (Col-0) roots.
b, Co-IP of pAHA2::AHA2-GFP from roots, followed by Western blot detection of TMK1 and Thr947-phosphorylated AHA2 on roots mock or 100 nM IAA-treated for 30 minutes. Interaction does not depend on auxin presence, but auxin-induced phosphorylation of the interacting AHA2 was observed. As a control sample we include input of of pAHA2::AHA2-GFP roots.
c, Bimolecular Fluorescent Complementation (BiFC) in Nicotiana benthamiana leaves transiently transformed either with TMK1-YFPN (TMK1 in pSPYNE), YFPC-AHA2 (AHA2 in pSPYCE) or both. Scale bar = 10 μm.
d, Differentially detected phospho-sites of AHAs in tmk1-1 normalized to WT (Col-0) MS detection levels. We observe less phosphorylation on the indicated phospho-sites in AHA1, AHA2 and AHA3 in the tmk1-1 mutant. Green indicates the sites with known activation function, while orange is used for known inhibitory function. n= 4. Box plot depicts minimum to maximum, mean ± SD. Two-sample t-test (part of MaxQuant-Perseus analysis).
e, Western blot analysis of auxin-induced AHA2 Thr947 phosphorylation in WT and tmk1-1 roots treated with 100 nM IAA for 1 hour. AHA2 levels were determined as a control.
f, Quantification of the auxin effect on AHA2 phosphorylation in (d) by normalising the intensity ratio of pThr947 to AHA2 in auxin-treated root samples to the same ratio in mock-treated samples of the respective genotypes.
g, Western blot detection of the AHA2 levels and its Thr947 phosphorylation in full seedlings shows reduced AHA2 phosphorylation in tmk1,4 compared to WT.
h, Auxin-induced ATP hydrolysis activity is impaired in tmk mutants relative to WT roots (1 hour mock or 100 nM IAA treatment). The IAA-treated sample was normalized to the mock-treated WT. Means of 3 biological replicates + SD. *p≤0.05, ns p>0.05, One-way ANOVA.