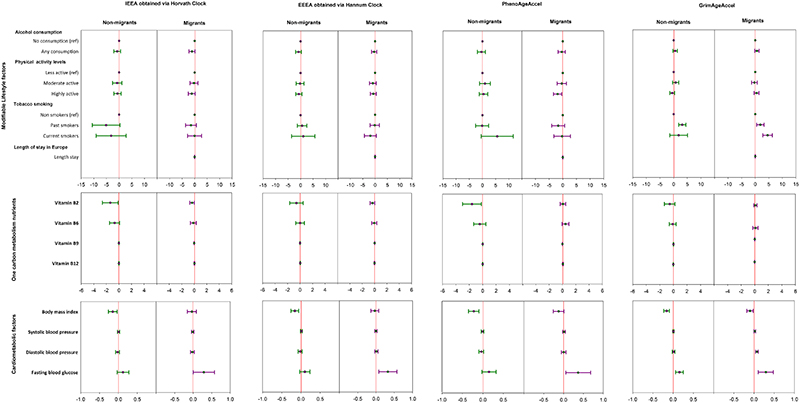
Figure 4. Forest plots of crude regression model β (and 95% confidence intervals) relating EAA measures to cardiometabolic related traits in the RODAM study.
The plot depicts regression model β with 95% confidence intervals in linear regression models adjusted for age, sex, education, smoking, physical activity, alcohol intake, total energy intake, and duration of stay in host countries for migrants, respectively. N=365 for migrants and 347 for non-migrants. Red line = reference line for confidence intervals. Abbreviations: IEAA= Intrinsic epigenetic age acceleration, EEAA= extrinsic epigenetic age acceleration, PhenoAge Accel= Pheno Age Acceleration, GrimAge Accel= Grim Age Acceleration. ref= reference, physical activity activity levels categorized according to Global Physical Activity Questionnaire (GPAQ) criteria. Vitamin intake was measured in mg/day for Vitamin B6 and Vitamin B12, while vitamin B9 and Vitamin B12 were measured in mcg/day. body mass index in kg/m2, fasting blood glucose in mmol/L, blood pressure in mmHg, Length stay= duration of stay in Europe for migrants. Reference (comparison) groups for modifiable risk factors: smoking = non-smokers, alcohol consumption = no (never) alcohol consumption, physical activity= less physically active.