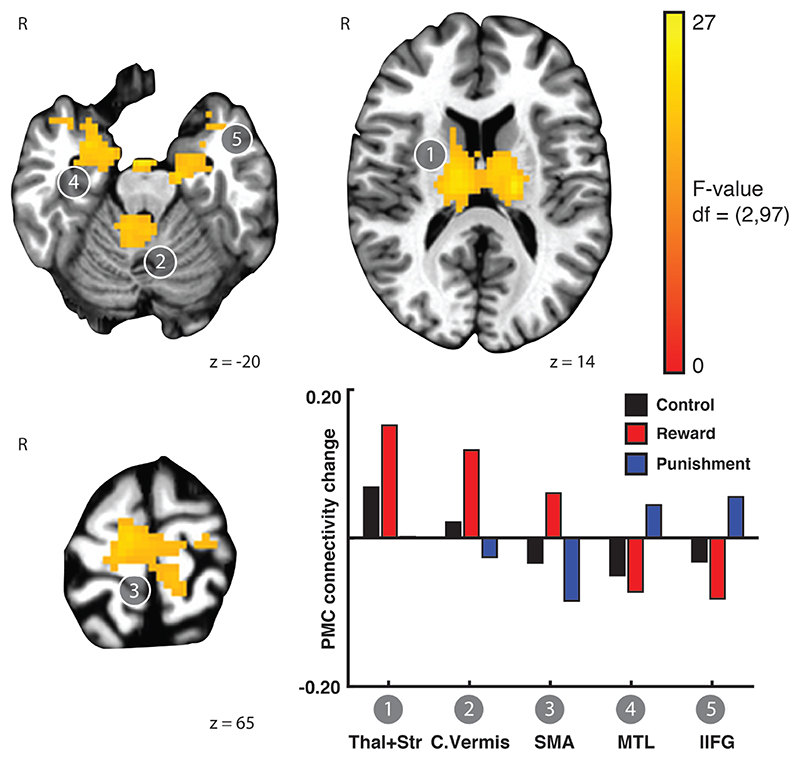
Figure 2.
Reward and punishment differentially affect PMC functional connectivity change after training on the SRTT. Linear mixed effects modelling revealed brain regions that exhibited a Rest x Feedback valence interaction in the functional connectivity of left PMC. Functional connectivity between PMC and the thalamus and striatum, cerebellum, and SMA increased after training with reward and control feedback but decreased after training with punishment. In contrast, functional connectivity between medial temporal lobe and left inferior frontal gyrus increased after training with punishment but decreased after training with reward and control feedback. Bars showing mean connectivity change across voxels in the identified cluster after training estimated by the linear mixed effects model are included to enable qualitative comparison and reveal the nature of the interaction effect.