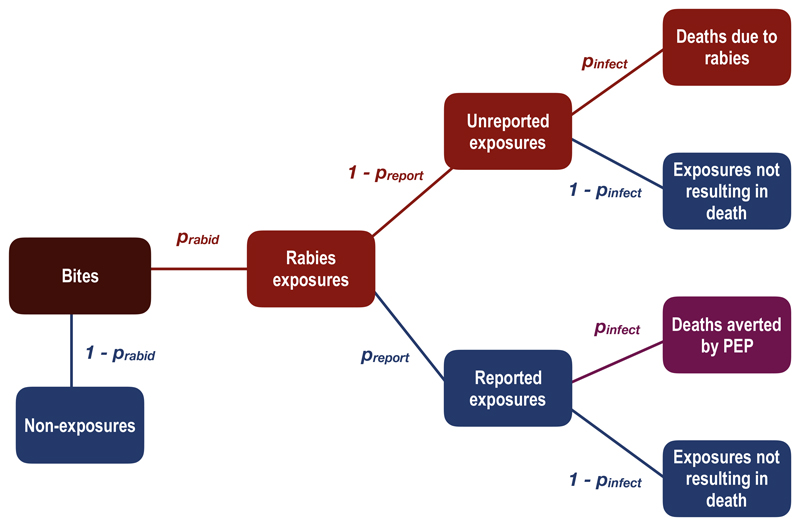
Fig. 1. Adapted decision tree framework to estimate burden of human rabies deaths and deaths averted by PEP.
We considered that some proportion of total bites in the population (expected bites annually, dark red box) are genuine rabies exposures (Bites × prabid = Rabies exposures), and non-exposures ((1 - prabid) × Bites) do not contribute to rabies deaths or averted deaths. Of the genuine rabies exposures, a fraction present to an ARMC and all of these persons receive PEP (Rabies exposures × preport = Reported exposures). Some of these exposed persons would otherwise have become infected and died if they had not received PEP (Reported exposures × pinfect = Deaths averted by PEP). Of the unreported exposures, a proportion will die due to rabies infection (Unreported exposures × pinfect = Deaths due to rabies). (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)