Figure 1.
Phenotypic and molecular landscape of a PDAC organoid biobank
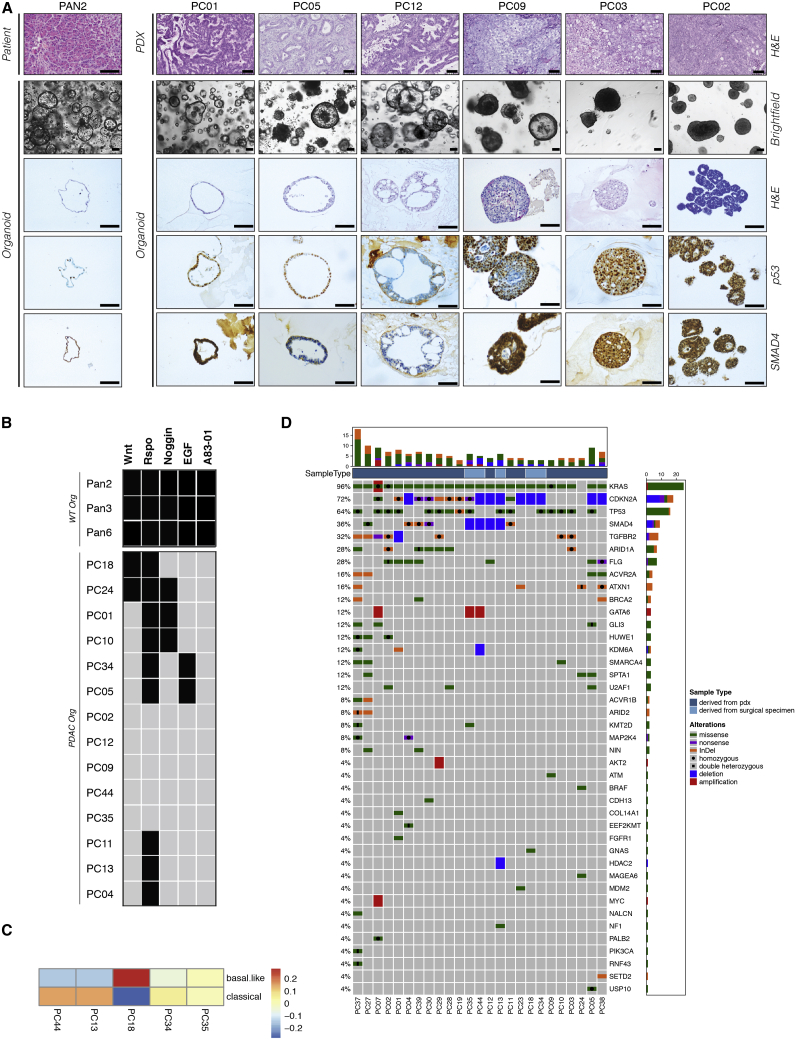
(A) Brightfield images and corresponding H&E, p53, and SMAD4 stainings for one WT pancreas organoid line and several PDAC organoid lines. Corresponding in vivo phenotype is shown from patient or PDX tissue. Scale bar: 100μm.
(B) Growth factor dependencies of different PDAC and WT organoid lines after in vitro culture for 6 passages in growth factor depleted medium. Black box = growth factor dependent, gray box = growth factor independent.
(C) Classification of PDAC organoids into either a basal-like or classical subtype based on RNA-seq profiles (Spearman correlation) using classification system by Puleo et al., 2018.29
(D) Overview of mutations in PDAC driver genes observed in PDAC organoid lines of our biobank (see Table S2 for a full list of PDAC driver genes). PDAC organoids derived from surgical specimens are shown in brown, those derived from PDX-cell suspensions are shown in violet. The following mutations are indicated: SNVs (green), InDels (violet), amplifications (red), and deletions (blue). The bar plots on the top depict the number of alterations in each sample, and the bar plots on the right depict the alteration frequencies for each gene in the biobank.