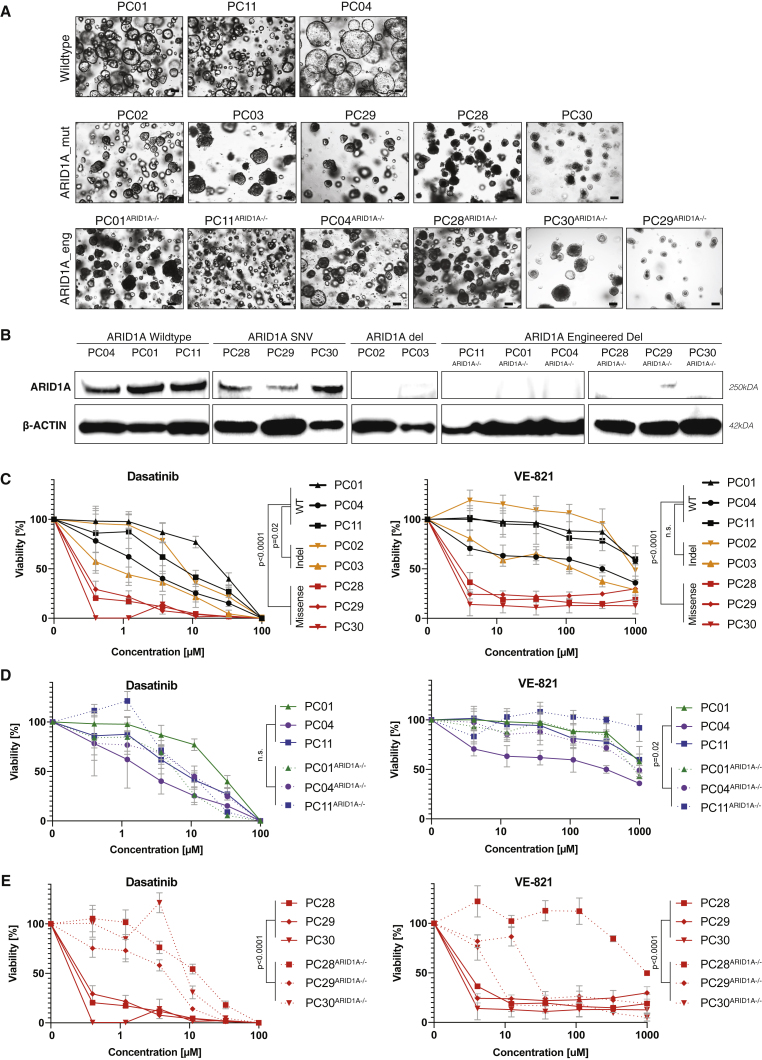
Figure 3.
Assessment of ARID1A drug-gene interactions in PDAC organoids
(A) Phenotypes of PDAC organoids WT for ARID1A (top panel), mutant for ARID1A (middle panel), and engineered by CRISPR-Cas9 to become mutant for ARID1A (bottom panel). While ARID1A mutations in PC28 and in PC30 are recurrent tumor driver mutations (cBioPortal database), the mutation in PC29 has not yet been reported in pan-cancer or PDAC studies (cBioPortal database), or as a SNP in healthy populations (dbSNP, NCBI database). Scale bar: 100μm.
(B) Western blot showing ARID1A and β-ACTIN expression.
(C) Response profile of genuine ARID1A mutant organoids (yellow, red) and ARID1A-WT organoids (black) to dasatinib (left panel) and VE-821 (right panel). Viability was normalized to solvent control (0.1% DMSO). Data is represented as means ± SDs based on technical and biological replicates.
(D) Response profile of ARID1A-WT organoids (full lines) and CRISPR-Cas9 engineered ARID1A mutant organoids (dashed lines) to dasatinib (left panel) and VE-821 (right panel). Viability was normalized to solvent control (0.1% DMSO). Data plotted for ARID1A-WT organoids was derived from the same experiment as shown in C. Data is represented as means ± SDs based on technical and biological replicates.
(E) Effect of introducing an ARID1A frameshift mutation in three organoid lines that initially contained a missense mutation on dasatinib (left panel) and VE-821 (right panel) treatment. Viability was calculated by normalizing each dose to the DMSO treated control. Data plotted for ARID1A-missense organoids was derived from the same experiment as shown in (C). Data is represented as means ± SDs based on technical and biological replicates.
See also Figure S3. Two-way ANOVA was used to compute the indicated p values comparing the drug-response of the indicated samples.