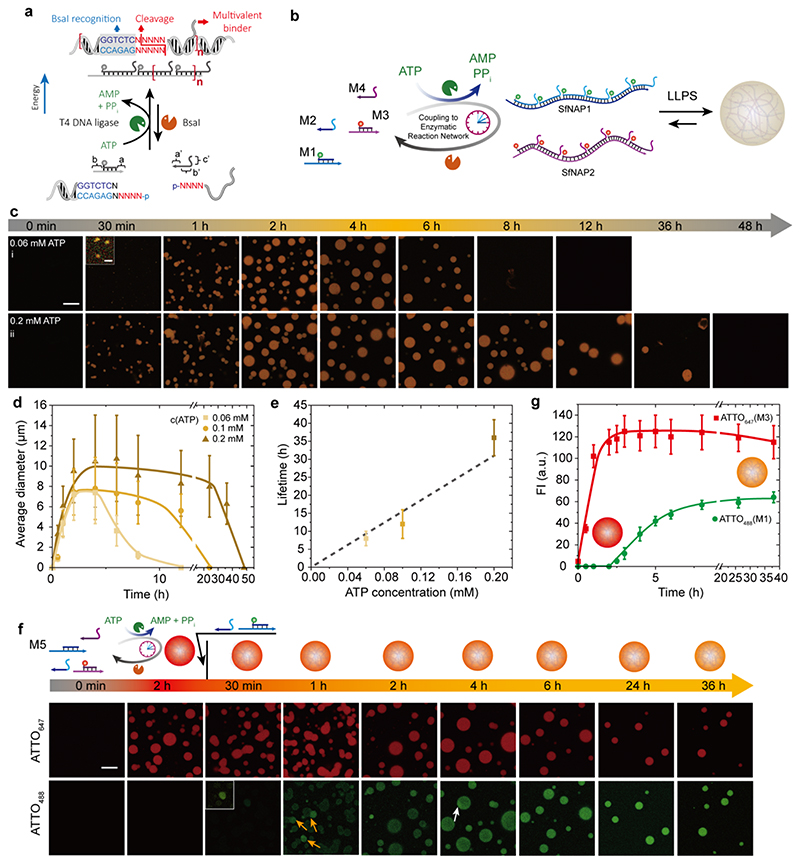
Figure 3. ATP-driven transient all-DNA coacervates with programmable lifetimes.
(a) Schematic illustration of the ERN furnishing an ATP-driven transient SfNAP. (b) Schematic illustration of ATP-driven membrane-less all-DNA coacervates via LLPS driven by transient multivalency of orthogonal SfNAPs. (c) Time-dependent CLSM measurements for transient all-DNA coacervates with programmable lifetimes by fueling with varied concentration of ATP (0.06 and 0.2 mM). CLSM measurements were conducted consecutively with the same microscopy settings. Scale bar = 20 μm; insert = 2 μm. (d) Time-dependent size of the transient coacervates with programmable lifetimes. Error bars are standard deviations from three random fields of view of duplicate experiments. Lines are guides to the eye. (e) Lifetimes are controlled by the ATP concentrations. Error bars are standard deviations of duplicate measurements. Line is a guide to the eye. (f) Tile integration and dynamization during a running transient coacervates system. The tile with ATTO488 was added 2 h after starting the initial system. CLSM before and after adding the ATTO488 tile confirm the integration and reconfiguration. Scale bar = 20 μm. (g) Time-dependent fluorescence intensities. Error bars are standard deviations from three random fields of view of duplicate experiments. Lines are guides to the eye. Conditions for (b): 37°C, 0.01 mM M1, 0.012 mM M2, 0.01 mM M3, 0.012 mM M4, 0.92 WU/μL T4 DNA ligase, 1.0 U/μL BsaI, and varying amounts of ATP, under orbital shaking at 80 rpm. Conditions for (f) 37°C, 0.01 mM M5, 0.012 mM M2, 0.01 mM M3, 0.012 mM M4, 0.92 WU/μL T4 DNA ligase, 1.0 U/μL BsaI, and 0.2 mM of ATP, under orbital shaking at 80 rpm, followed by addition of another 0.002 mM M1 and 0.0024 mM M2 after 2 h running of the transient coacervation reaction.