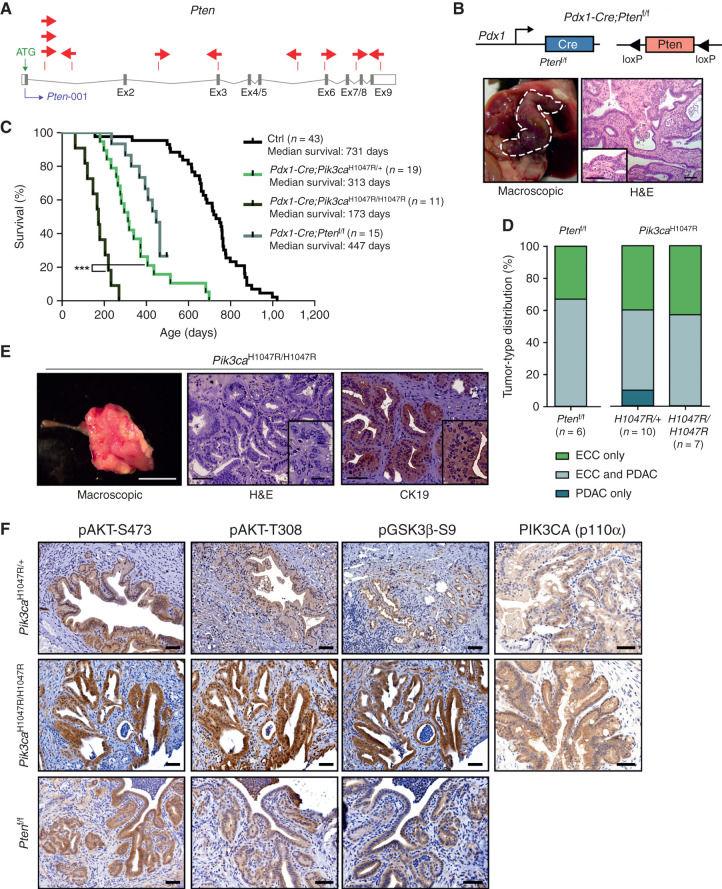
Figure 5.
Functional validation of transposon integrations: PI3K signaling output is a critical determinant of ECC development. A,piggyBac insertion patterns in Pten. Pten possesses one protein-coding isoform consisting of nine exons. Each arrow represents one insertion and indicates the orientation of the CAG promoter that was introduced into the transposon. B, Top: genetic strategy used to inactivate Pten in the Pdx1 linage using a Pdx1-Cre line. Bottom: representative macroscopic picture (left, bile duct depicted by a white dashed line) and hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)–stained tissue section (right) of an ECC from a Pdx1-Cre;Ptenf/f mouse. Scale bars, 50 μm for micrographs and 50 μm for insets. C, Kaplan–Meier survival curves of the indicated genotypes (***, P < 0.001, log-rank test). The Pdx1-Cre;Pik3caH1047R/+ and the control cohort are the same as those shown in Fig. 2C. D, Tumor-type distribution according to histologic analysis of the bile duct and pancreas from Pdx1-Cre;Ptenf/f, Pdx1-Cre;LSL-Pik3caH1047R/+, and Pdx1-Cre;LSL-Pik3caH1047R/H1047R mice. The Pdx1-Cre;Pik3caH1047R/+ cohort is the same as shown in Fig. 2D.E, Left: representative macroscopic picture of an ECC from a Pdx1-Cre;LSL-Pik3caH1047R/H1047R mouse. Scale bar, 1 cm. Middle and right: representative H&E-stained (middle) and IHC CK19–stained (right) tissue section of an ECC from a Pdx1-Cre;Pik3caH1047R/H1047R mouse. Scale bars, 50 μm for micrographs and 20 μm for insets. F, Representative H&E stainings and IHC analyses of PI3K/AKT pathway activation and Pik3ca (p110α) expression in the common bile duct of Pdx1-Cre;LSL-Pik3caH1047R/+, Pdx1-Cre;LSL-Pik3caH1047R/H1047R, and Pdx1-Cre;Ptenf/f mice. Scale bars, 50 μm.