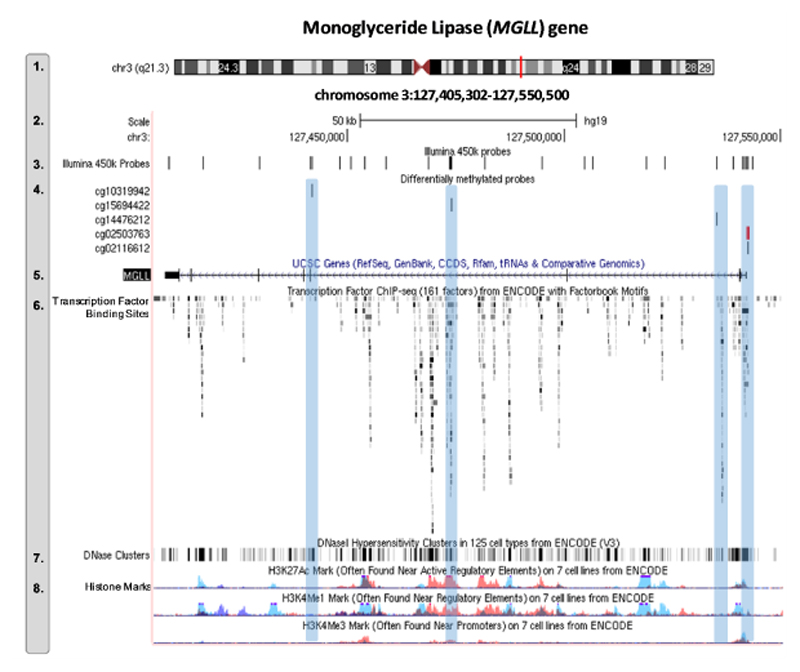
Figure 2. Functional characterization of MGLL DNA methylation sites associated with early-onset conduct problems.
Expanded views from the UCSC genome browser of the MGLL gene showing the position of the DNAm sites associated with early-onset CP relative to ENCODE regulatory elements. Track numbers are displayed on the left-hand site, and represent the following (1) genomic positon of MGLL in chromosome 3; (2) genomic coordinates and scale; (3) location of all Illumina 450k probes that map onto the MGLL gene (n = 26); (4) location of differentially methylated probes associated with early-onset vs low conduct problems (n = 5). These are highlighted in blue to facilitate comparison with the regulatory elements displayed in lower tracks (track 6-8). In red is the probe that survived genome-wide correction (MGLL cg02503763; all other probes significant at p<0.05); (5) schematic representation of the MGLL gene; (6) location of transcription factors (based on ChIP-seq data from 91 cell types), where darker shades indicate a stronger signal occupancy; (7) DNaseI hypersensitivity clusters (based on ChIP-seq data from 125 cell types), where darker shades also indicate a stronger signal; and (8) levels of enrichment of three histone marks (H3K27Ac, H3K4Me1, and H3K4Me3) across three cell-types, including blood (GM12878 [red], K562 [purple]) and umbilical vein endothelial (HUVEC [blue]) cells.