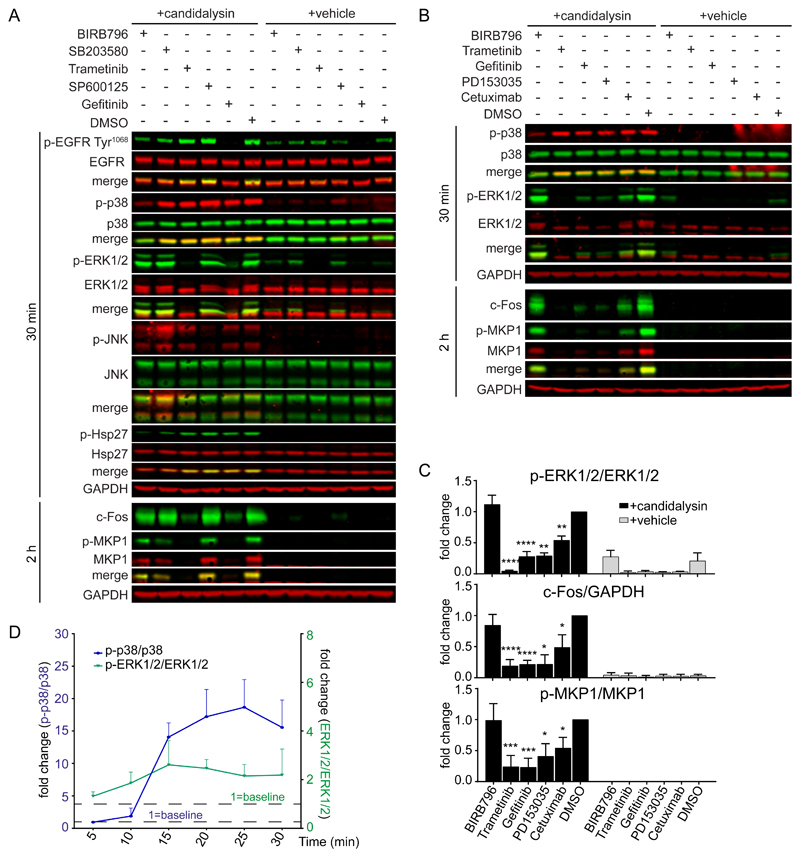
Fig. 1. Candidalysin activates p38 independently of the EGFR-ERK1/2-c-Fos pathway.
A, Representative immunoblot showing phosphorylated (p-) and total EGFR, p38, ERK1/2, JNK, and Hsp27 at 30 min and c-Fos induction and MKP1 phosphorylation at 2 h after candidalysin stimulation of TR146 OECs in the presence of BIRB796, SB203580, SP600125, Trametinib, Gefitinib, or DMSO. B, Representative immunoblot showing phosphorylated and total p38, ERK1/2, and MKP1 and c-Fos induction the indicated times after candidalysin stimulation in the presence of BIRB796, Trametinib, Gefitinib, PD153035, Cetuximab, or DMSO. Immunoblots are representative of three biological replicates (two for MKP1 in A). GAPDH is a loading control. C, Graphical quantification of immunoblots as in B. Graphs show means of three biological replicates + SD and are expressed as fold change relative to DMSO + candidalysin. D, Time-course of p38 and ERK1/2 phosphorylation following candidalysin stimulation. Data are means of three biological replicates + SD and are expressed as fold change relative to baseline amounts at 5 min post-candidalysin stimulation. Statistical significance for C was quantified by one sample t test compared to a hypothetical value = 1. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.