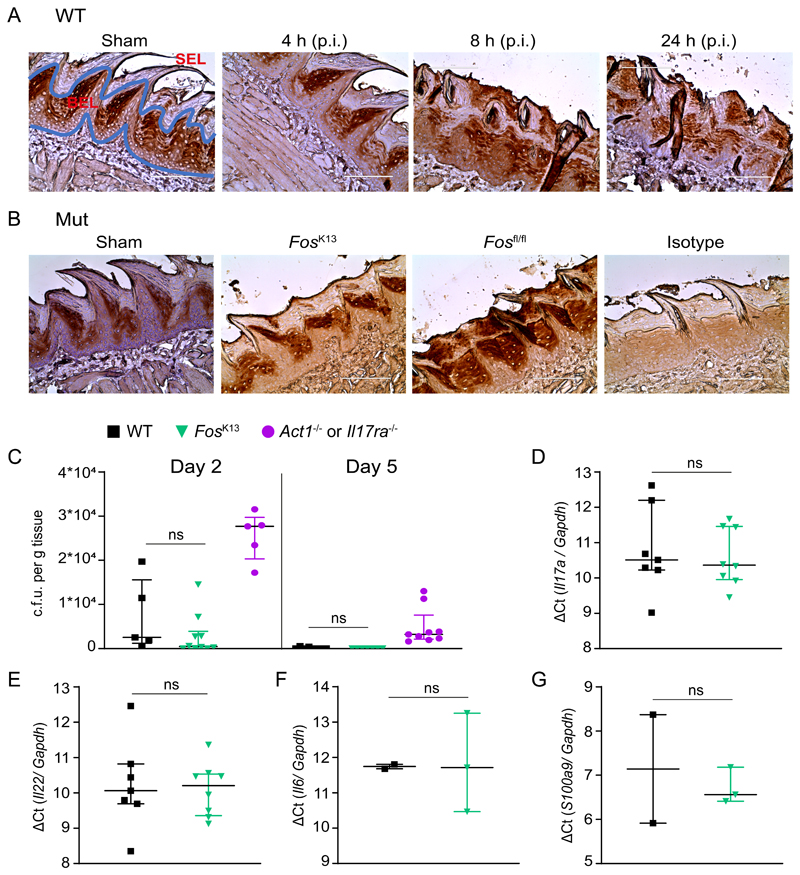
Fig. 7. c-Fos induction is not required for host immunity against C. albicans.
A, Wild-type mice (WT; C57BL/6) were subjected to sham infection (PBS) or OPC and tongues were harvested at the indicated time points post-infection (p.i.) for c-Fos staining by immunohistochemistry (IHC). SEL, suprabasal epithelial layer; BEL, basal epithelial layer. Scale bar, 100 μm. B, IHC for Fos in tongues of epithelial-specific Fos knockout (FosK13) mice mock-infected (sham) or subjected to OPC. Tissues from infected unrecombined floxed control (Fosfl/fl) mice and tissues from infected FosK13 mice stained with an isotype-matched antibody (isotype) are shown as positive and negative controls, respectively. Images are representative of at least two sections from individual mice. Scale bar, 100 μm. C, Fungal burdens from tongues of Fosk13 mice sublingually infected with C. albicans 2 and 5 days p.i. Results are median ± interquartile range of 5-10 mice per group obtained over two (for day 2) or three (for day 5) independent experiments (Mann-Whitney tests). D to G, Relative expression of Il17a (D), Il22 (E), Il6 (F), and S100a9 (G) in mouse tongue homogenates 1 day p.i. mRNA amounts were determined by ΔCT method and normalized to Gapdh. Results are median ± interquartile range of 2-8 mice per group obtained over two for D and E or one for F and G independent experiments (Mann-Whitney tests). Each symbol represents one mouse.