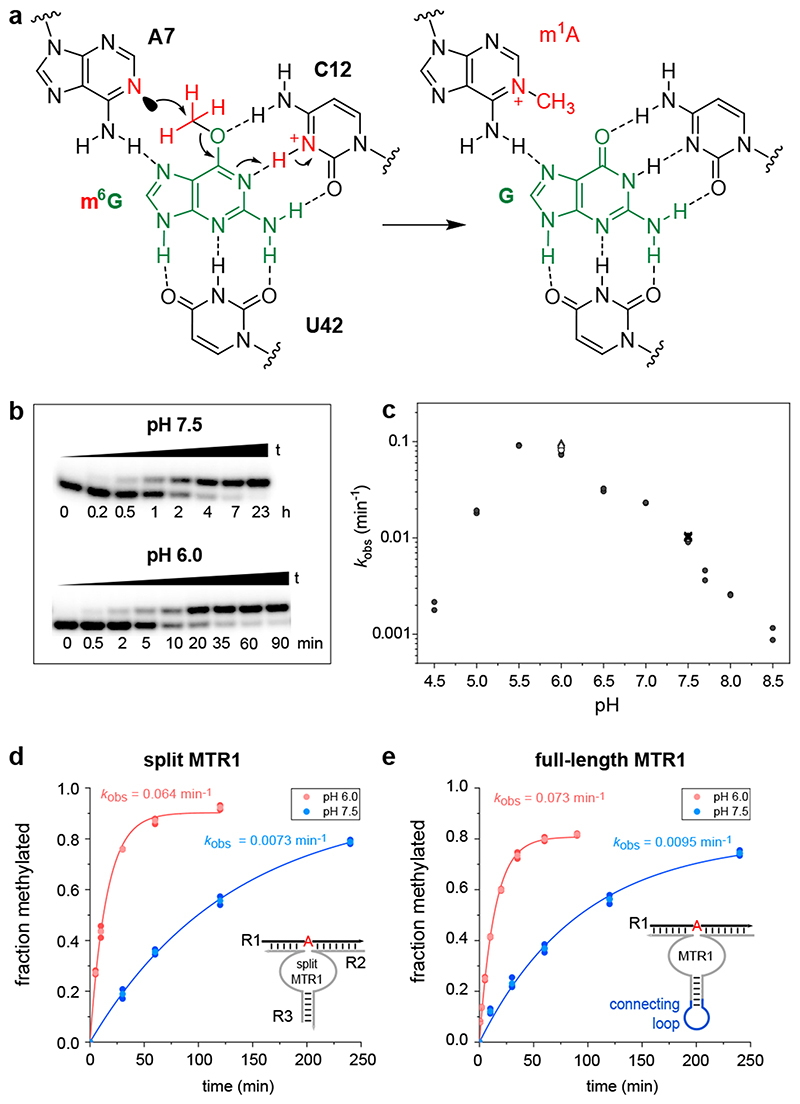
Fig. 3. The methyltransferase ribozyme employs general acid catalysis.
(a) A protonated cytidine is suggested in the active site for RNA-catalysed methyl group transfer. The mechanism involves the nucleophilic attack of the nitrogen lone pair (N1 of A7) on the methyl carbon (at O6 of m6G). The guanine leaving group accepts a proton from cytidine C12+, resulting in a positive charge on m1A and a standard G:C hydrogen bonding pattern in the product state. (b) Representative PAGE images of the kinetic assays from 3 independent experiments with split MTR1 at pH 6.0 and pH 7.5 under single-turnover conditions. (c) pH rate profile for split MTR1 (n = 2 or 3, individual data points for each buffer (different symbols for same pH indicate different buffers used; for details see methods section and source data). (d, e) Comparison of methyl transfer rates for split (d) and full-length (e) MTR1, reaction with m6G at pH 6.0 (red) and pH 7.5 (blue). Conditions in b-e) 5'-32P-labeled R1, 10 μM MTR1, 100 μM m6G, 40 mM MgCl2, 25°C.